Highlights
- Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is a heart condition where the upper sections of the heart beat faster and with an irregular rhythm compared to the lower sections.
- Between 2 and 3 percent of the population experiences AFib, with up to half not even realizing it’s a condition.
- Symptoms of AFib include a racing or pounding heartbeat, shortness of breath, and weakness, but many people have no symptoms at all.
- Managing AFib and the anxiety around it involves lifestyle changes, working with your doctor, and getting the lowest prices on atrial fibrillation medications.
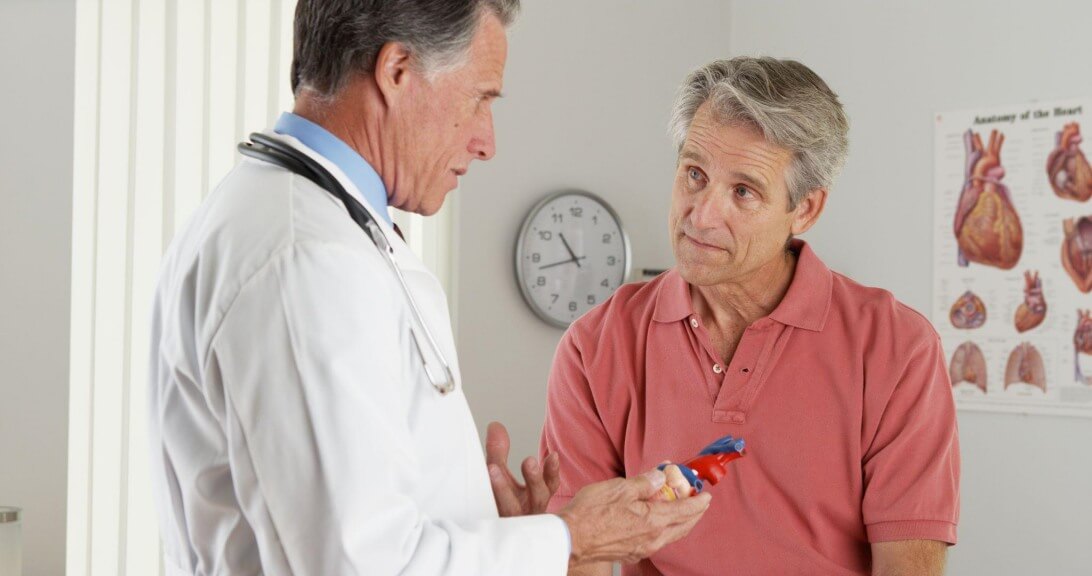
Atrial fibrillation is a common heart ailment, yet many of us aren’t sure what it is or why it’s a cause for concern. If you’re not sure what atrial fibrillation is or whether you need to get checked for it, learn how it’s diagnosed, what the symptoms are, and how you can manage the condition.
What Is Atrial Fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation (also called AFib) is an abnormal heart rhythm, where one or both of the heart’s upper sections, the atria, beat faster and irregularly compared with the lower chambers. It affects approximately 2 to 3 percent of people in the U.S.
There are three types of atrial fibrillation:
- Paroxysmal AFib. This occurs intermittently and stops on its own within seven days.
- Persistent AFib. Atrial fibrillation that lasts longer than seven days is considered persistent. This is often treated by applying electric shocks to the heart.
- Long-standing persistent AFib. In this type, AFib lasts longer than a year.
Causes of Atrial Fibrillation

While approximately half of all AFib cases don’t have a notable cause, as of this writing, there are several common ones to be aware of. They include:
- Genetics. If you have a family history of AFib or congenital heart disease, you’re at higher risk of developing all types of AFib.
- Tobacco use. Due to its impact on the cardiovascular system, tobacco can raise the risk of triggering AFib in those predisposed and raise the chances of an otherwise healthy person developing AFib.
- Alcohol consumption. Excessive alcohol use can trigger AFib. Long-term heavy alcohol use can cause changes to the heart and circulatory system that make AFib more likely.
- Hyperthyroidism. Excessive production of thyroid hormone can overstimulate the heart. If you’re diagnosed with hyperthyroidism or have a family history, discuss what to monitor with your doctor.
- Other chronic conditions. While the connections between conditions such as obesity, diabetes, obstructive sleep apnea, and other common conditions are still being researched, there is a clear link between these conditions and AFib.
- Some medications. Some over-the-counter medications, such as ibuprofen, and some prescription medications, particularly chemotherapy drugs, may raise the risk of AFib.
Symptoms of Atrial Fibrillation
AFib can often present without symptoms. In some cases, patients only learn they have AFib due to routine testing for other heart conditions, or when they undergo a routine test, such as an electrocardiogram, that’s performed as part of a physical.
Some common symptoms experienced include:
- Heart palpitations
- Chest pain
- Exercise intolerance
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath while lying flat
- Sudden onset of shortness of breath during the night or while sleeping
- Swelling in the limbs or extremities
- Dizziness
- Lightheadedness
If you experience any of these symptoms without another explanation, particularly if they’re ongoing problems or two or more symptoms occur together, seek medical attention immediately.
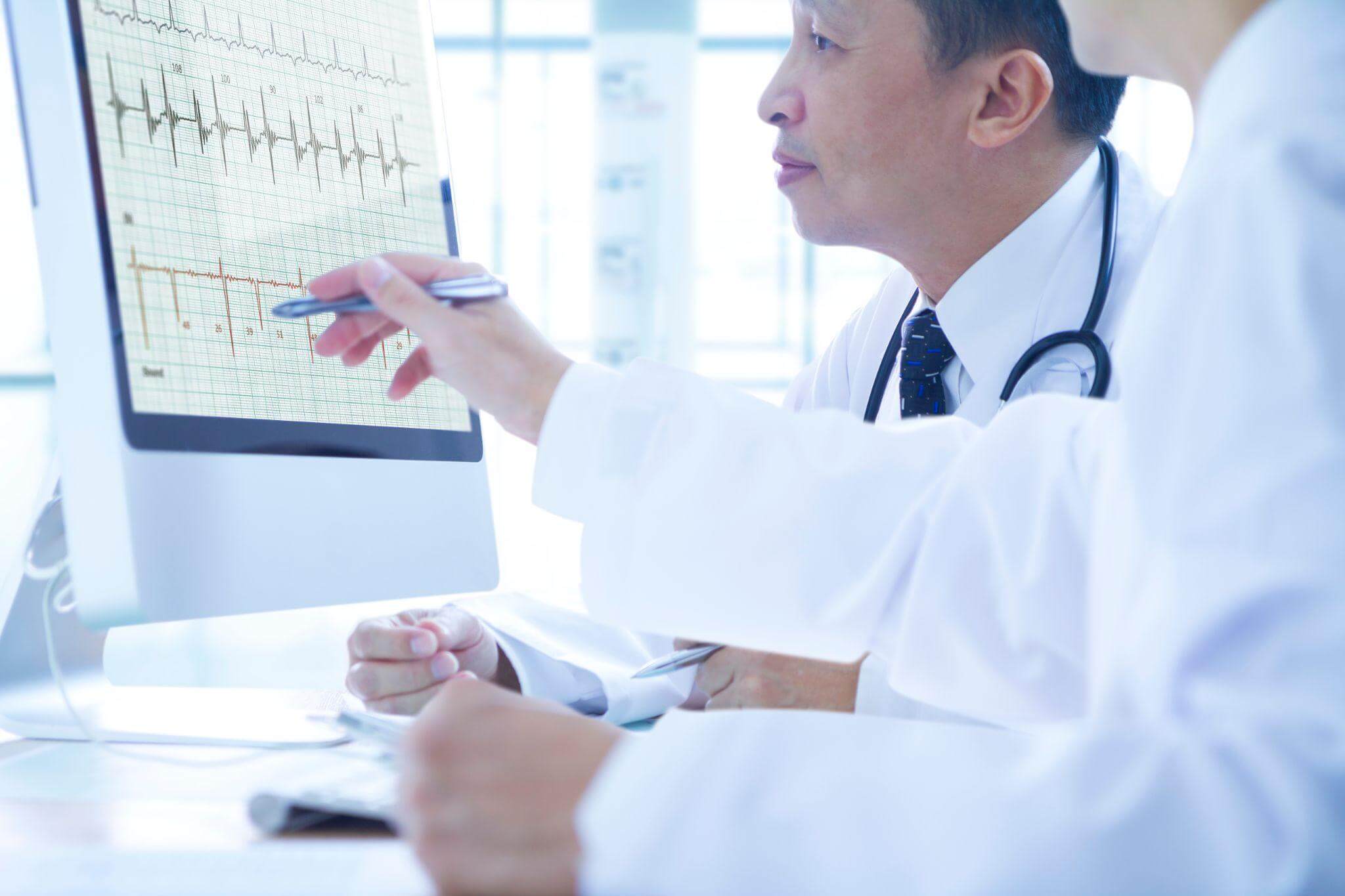
Diagnosis of Atrial Fibrillation
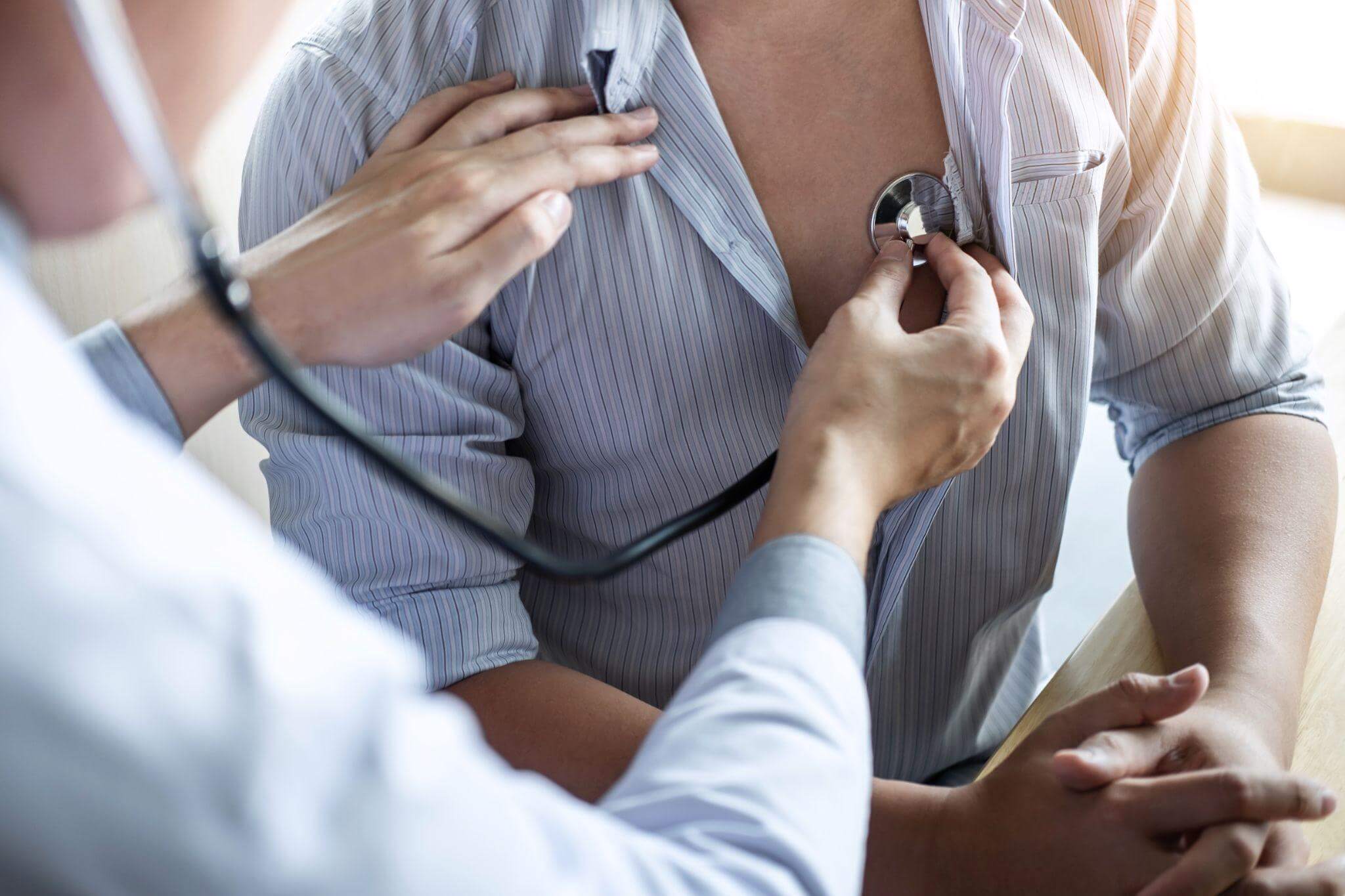
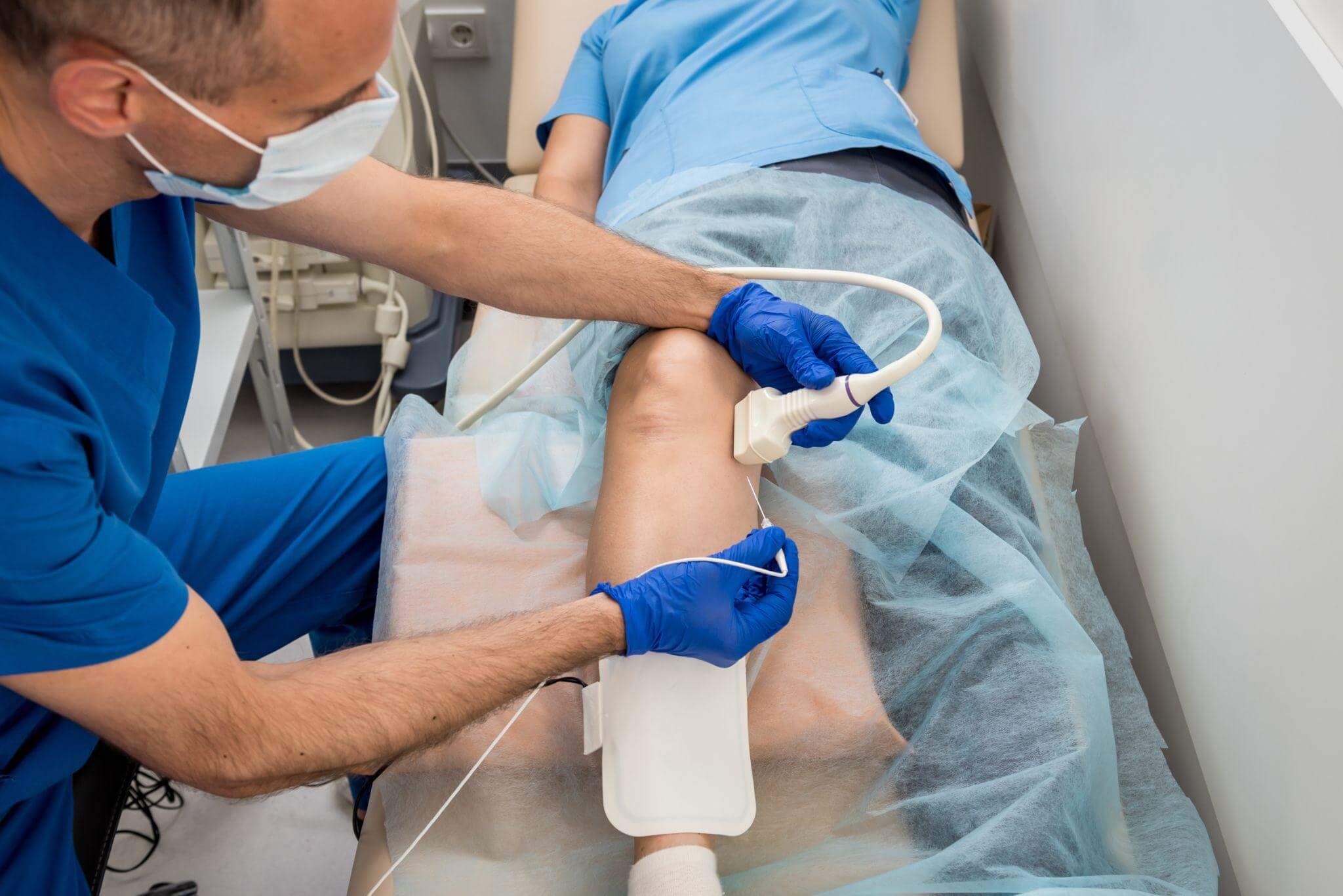
To diagnose AFib, particularly asymptomatic AFib, you’ll need to undergo a series of tests. Several of these are part of a routine physical screening. Others can be added to routine lab work as needed.
Tests your provider may order include:
- Blood tests. If your doctor doesn’t order them, request tests for kidney function, electrolytes, thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), and a blood count. If you’re experiencing chest pain, inform your doctor, as you may need other blood tests, as well.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG). A record of the heart’s electrical activity can spot AFib quite easily, although several other types of arrhythmia may be possible.
- Echocardiogram (TTE). Essentially an ultrasound of the heart, this is used on newly diagnosed cases of AFib to determine the overall state of the heart and whether other forms of heart disease are present.
If your provider believes the cause of your AFib is reversible, they may order additional testing.
Risk Factors of Atrial Fibrillation
In addition to causes listed above, the following are risk factors for AFib, some of which can be mitigated.
- Sedentary lifestyle. Lack of exercise can change the structure of the heart and make AFib more likely, but this can be addressed with a regular light exercise program. Too much sitting can also contribute to secondary causes of heart disease, such as obesity.
- Sleep disorders. Common sleep disorders, such as obstructive sleep apnea or unusual waking and sleeping hours, can increase the chances of AFib.
- Hypertension. High blood pressure increases the overall stress on the body and raises your risk of developing AFib.
- Lung diseases. While researchers are still investigating this connection, evidence points to certain lung diseases contributing to both the onset and severity of AFib.
Having any of these risk factors is not a guarantee that you will develop AFib, but one or more of them will increase your risk.
Complications of Atrial Fibrillation
The most notable complication of AFib is an increased risk of stroke due to clots forming in the atria and traveling to the brain. Other chronic conditions, like diabetes, can raise this risk even further.
Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation
AFib treatment usually consists of a combination of approaches. With some types of AFib, your doctor may recommend starting with less-invasive treatment options.
Treatment approaches for atrial fibrillation include:
- Lifestyle changes. Changes to diet, increasing exercise, quitting smoking, and cutting alcohol consumption are standard approaches to AFib of all types.
- Comorbidity management. Treatment of other conditions that increase the risks associated with AFib can help mitigate risks.
- Cardioversion. In extreme cases or for AFib that presents serious risk, electric current or chemicals can regulate the heartbeat.
- Surgery. Some surgical procedures can remodel the heart and help it to beat normally.
- Medication. Medication can restore an irregular heartbeat and prevent clotting.
BidRX Can Help You Find The Lowest Prices for Atrial Fibrillation Medication
Managing AFib shouldn’t dominate how you live your life, and the cost of medication shouldn’t be a source of anxiety as you figure out how to best care for yourself. BidRX helps you find the lowest price for all your medications. Enter your medication, and pharmacies around the nation will bid on your business. You choose the option you prefer, and the winner will ship your prescription to your door, or you can pick it up locally, depending on the bid you choose.
BidRX can take the work out of managing your prescriptions and your budget. To get started, visit our medication page and create your bid today.
