Highlights
- Gallstones are small, hardened bits of cholesterol or bilirubin that form in the gallbladder.
- Gallstones affect 10-15 percent of the American population.
- Women and individuals over the age of 40 are at a higher risk of developing gallstones.
- Gallstones may not cause any symptoms at first but can create serious complications if left untreated.
- Treatments for gallstones include surgery, non-surgical procedures, and medications.
Gallstones will occur naturally in nearly 25 million people — about 10-15 percent of the American population. They’re more common in women and are more likely to occur as you age. These small “stones” develop in the gallbladder and can go undetected for a long time.
So why should you be concerned about gallstones if you don’t even notice them?
Let’s explore more about what gallstones are, how they form, how they impact your health, and what you can do to treat or prevent them.
What Are Gallstones?

The gallbladder stores bile, a fluid produced by the liver to help digest fats and absorb vitamins. Gallstones are hardened bits of bile that form when bile becomes supersaturated with cholesterol or other components and crystallizes.
There are two types of gallstones:
- Cholesterol gallstones. Primarily made of hardened cholesterol. This is the most common type, accounting for about 80-90 percent of gallstones.
- Pigment gallstones. Made of bilirubin, a substance produced when the liver breaks down red blood cells.
Gallstones can vary in size, from tiny grains of sand to large golf ball-sized formations.
Gallstone Symptoms
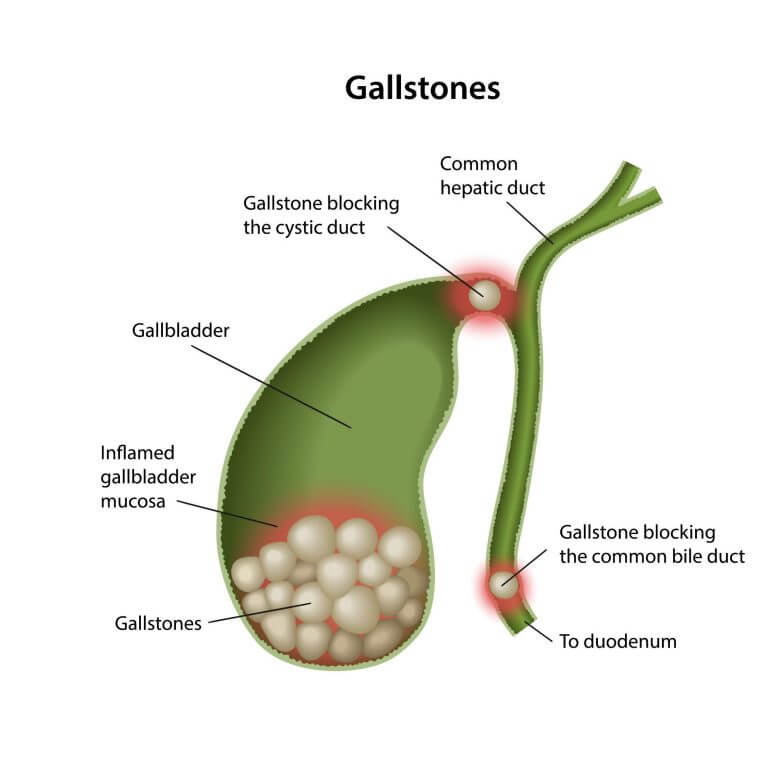
Many people with gallstones do not experience any symptoms. However, gallstones may eventually block the bile ducts, which can lead to:
- Sudden and intense pain in the upper right abdomen
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Fever
- Yellowing of the skin (jaundice)
- Chills
If you experience symptoms of gallstones, you should seek medical attention.
Gallstone Causes
The exact cause of gallstones isn’t fully understood. Cholesterol gallstones may form if the gallbladder doesn’t contract as it should, leaving bile behind. In some cases, there might be too much cholesterol in the gallbladder and not enough bile salts to dissolve it.
Pigment stones may form if you have liver disease, anemia, or an infection in the bile ducts. It’s not clear how pigment gallstones develop.
Your doctor will be able to differentiate between cholesterol gallstones and pigment gallstones. They may require testing and evaluations, such as examining bilirubin levels and cholesterol or imaging tests.
Gallstone Risk Factors
Certain individuals may be at a higher risk of developing gallstones, including:
- Being female
- Being age 40 or older
- Obesity
- Rapid weight loss
- Diabetes
- Eating a high-fat, high-cholesterol, low-fiber diet
- Having a family history of gallstones
- Having pre-existing conditions, such as cirrhosis of the liver, certain blood disorders, or certain gastrointestinal disorders
Talk to your doctor about other possible risk factors or to assess your risk level.
Gallstone Diagnosis
If you suspect you might have gallstones, your doctor can perform a series of tests and evaluations to reach a diagnosis. Options include but are not limited to:
- Ultrasound
- CT scan
- MRI
- Blood tests
- Clinical assessments
Your healthcare provider will determine the best tests and evaluations to reach a diagnosis.
Gallstone Complications