Highlights
- Levothyroxine (Synthroid) is a medication that corrects hormone deficiencies resulting from hypothyroidism.
- When your thyroid gland fails to produce enough hormones, levothyroxine supplements them to meet your needs.
- Many patients take levothyroxine for as long as they live.
- Find the lowest price for levothyroxine with bidRx.
When your thyroid gland doesn’t work well, your body has trouble regulating its metabolism and energy. If they find that to be the case, doctors may prescribe levothyroxine, a drug that provides more of the hormones your thyroid gland should make. Levothyroxine can make you feel better by rebalancing your hormones.
What Is Levothyroxine, and What Is It Used For?
Levothyroxine has been around for more than 70 years. First synthesized in 1949 and introduced in Germany in 1972, the drug gained FDA approval in 2002.
Levothyroxine is sold under several brand names, including Synthroid, Euthyrox, Levoxyl, Tirosint, and Unithroid.
Doctors use levothyroxine to treat the following diseases/conditions:
- Hypothyroidism, or a low thyroid hormone level, is the intended and primary target of this drug
- Enlarged thyroid gland (goiter)
- Hormone imbalances caused by lower-than-normal thyroid gland function
In addition to these uses, some doctors may use the drug for the off-label treatment of conditions like depression, female infertility, and obesity. Levothyroxine’s use for obesity is contraindicated. It can interact with diet pills and appetite suppressants and may even cause death.
How Does Levothyroxine Work?
Levothyroxine is a synthetic hormone that supplements thyroxine in people whose thyroid glands don’t produce enough of the hormone.
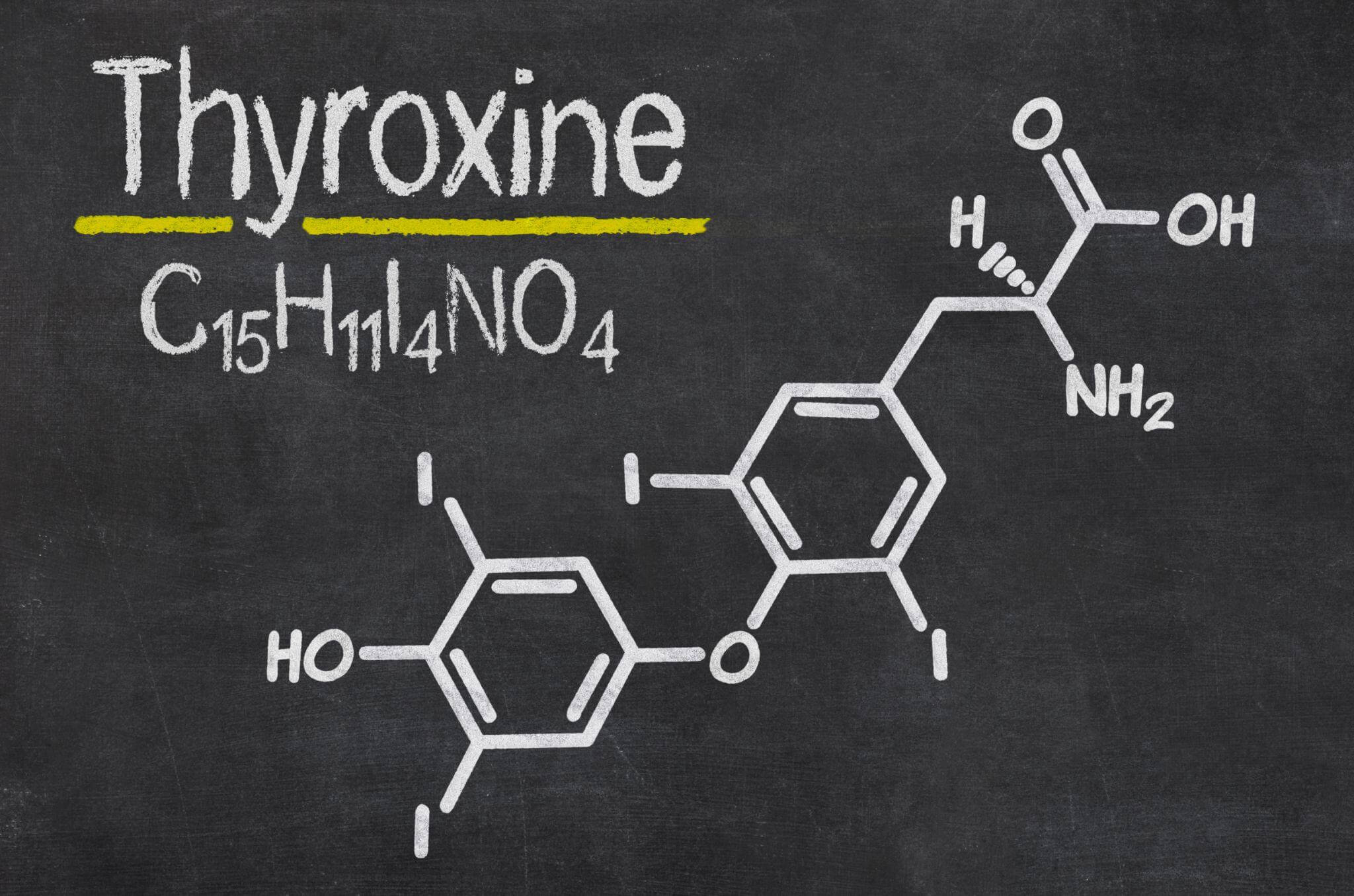
Once you ingest a dose of the drug, your digestive system absorbs it, and synthetic thyroxine gets into your bloodstream. From there, your liver converts it to triiodothyronine, the active form of the hormone. Triiodothyronine plays an active role in regulating your metabolism and energy levels.
Levothyroxine doesn’t help your thyroid gland produce more thyroxine; it’s an external supplement. Levothyroxine is a long-acting medication; it takes your body a while to absorb it and convert it to its active form.
What Formulas Are Available for Levothyroxine?
Levothyroxine is available all over the world. It comes in different formulas depending on the country, brand name, etc. It is available in the following formulations:
- Tablet. You can swallow levothyroxine tablets with water on an empty stomach, as your doctor recommends. A wide range of dosages are available in tablet form, from 25 micrograms to 300 micrograms.
- Capsules. Like tablets, capsules are for oral ingestion.
- Oral solution. Some patients can’t swallow tablets or capsules; they can take their levothyroxine doses through an oral solution.
- Intravenous solution. Hospitals can administer levothyroxine through IV to patients who can’t take the drug orally.
Levothyroxine Dosage and Administration
Always follow your doctor’s instructions when taking drugs like levothyroxine. Never take more or less than the recommended dose, and stick to the schedule your doctor recommends.
The factors that influence dosage are:
- The nature of your thyroid condition
- Other medical conditions you may have
- Cardiovascular status
- Age
- Pregnancy
- Clinical response to the medication
Healthy Adults
For otherwise healthy adults, the typical initial dose is 1.6 micrograms per kilogram of body weight, once a day. Doctors will observe parameters like your TSH (thyroid-specific hormone) levels and adjust doses until they normalize.
Adults Over 50 or With Heart Problems
For these patients, the initial dose is usually between 12.5 and 25 micrograms orally, once per day. Doctors will adjust dosage as the clinical response of the patient requires.
Adults with Severe, Long-term Hypothyroidism
The initial dose is generally 12.5 to 25 micrograms per day.
TSH Suppression in Adults
In adults, doctors may use a daily dose of 2 micrograms per kilogram of body weight to reduce TSH levels to below 0.1IU/L.
Older Adults
The starting dose for older adults is typically either 12.5 or 25 micrograms per day. Doctors will individualize dosage based on the health condition of patients. In this age range, co-occurring diseases are significant factors to consider.
Children
Health condition and age determine levothyroxine dosage for children, as follows:
- Newborns with a heart failure risk get a minimal dose that doctors will then tweak as the condition of the patient allows.
- Otherwise-healthy newborns typically get 10-15 micrograms per kilogram of body weight once per day up to the age of three months.
- The dose for children between three and six months is usually 8-10 micrograms per kilogram of body weight once per day.
- Children between 6 and 12 months will usually take 6-8 micrograms per kilogram of body weight.
- One- to five-year-olds are typically prescribed 5-6 micrograms per kilogram of body weight.
- The daily dose for 6-12-year-olds is usually 4-5 micrograms per kilogram of body weight.
- Children over 12 may get 1.6 micrograms or 2-3 micrograms per day, depending on whether they’ve begun puberty.
How Should I Take Levothyroxine?
Always follow all directions on the prescription label. If you are otherwise healthy and capable of swallowing, your provider will likely prescribe ooral levothyroxine.
Take the medication with a full glass of water on an empty stomach in the morning, before breakfast. Try to swallow the tablet quickly, as it may swell in your throat and cause discomfort.
If you’re taking an oral solution, measure it carefully with a syringe. Keep in mind that your doctor may tweak your dose if you gain or lose weight.
Hormonal processes are slow. The tablet may dissolve quickly in your stomach, but it can take weeks for the medication to make a difference in how you feel.
Keep taking the medicine even if you feel better. It merely supplements your hormone production; it does not cure your hypothyroidism. Many patients have to take levothyroxine for the rest of their lives.
Your doctor may order frequent blood tests to figure out how to optimize your dosage.
What Are the Potential Side Effects of Levothyroxine?
Like any drug, levothyroxine may cause an allergic reaction. Seek medical assistance immediately if you experience swelling in your mouth, tongue, throat, or face; hives; or difficulty breathing.
The severe side effects of the drug can be life-threatening, so treat them accordingly. Seek emergency medical help if you experience:
- Irregular heartbeats
- Shortness of breath
- Fever
- Insomnia
- Weakness
- Tremors
- Sweating
- Hot flashes
- Chest pain that spreads to the jaw or the arms
- Irritability
- Nervousness
- Dry skin
- Hair loss
- Vomiting
- Changes in appetite
- Diarrhea
- Irregular periods
- Weight loss
- Memory problems
Levothyroxine can cause many other severe side effects. If you are worried about your symptoms, contact your doctor immediately. Many of the side effects are more likely to appear in older adults.
Some of the less severe and more common side effects of the drug include:
- Increased appetite
- Weight loss
- Rashes
- Hot flashes
- Diarrhea
- Altered menstrual periods
- Leg cramps
- Headache
- Insomnia
- Nervousness
- Irritability
- Partial hair loss
Some of the rare side effects of levothyroxine include:
- Double vision
- Blurred vision
- Dizziness
- Severe headache
- Pain in the eyes
- Stopping or slowing growth in children
- Knee and hip pain
- Limping
- Seizures
Some of the common and light side effects of the drug do not require medical attention. If you find that these effects persist, however, you should still seek help.
- Crying
- A false sense of well-being
- Inexplicable fear and nervousness
- Warmth
- Muscle weakness
- Restlessness
- Mood swings
- The inability to get pregnant
- Discomfort
- Warmth
- Depression
Though these side effects aren’t severe, they should not persist. If they do, they may require your doctor’s attention.
What Should I Avoid When Taking Levothyroxine?
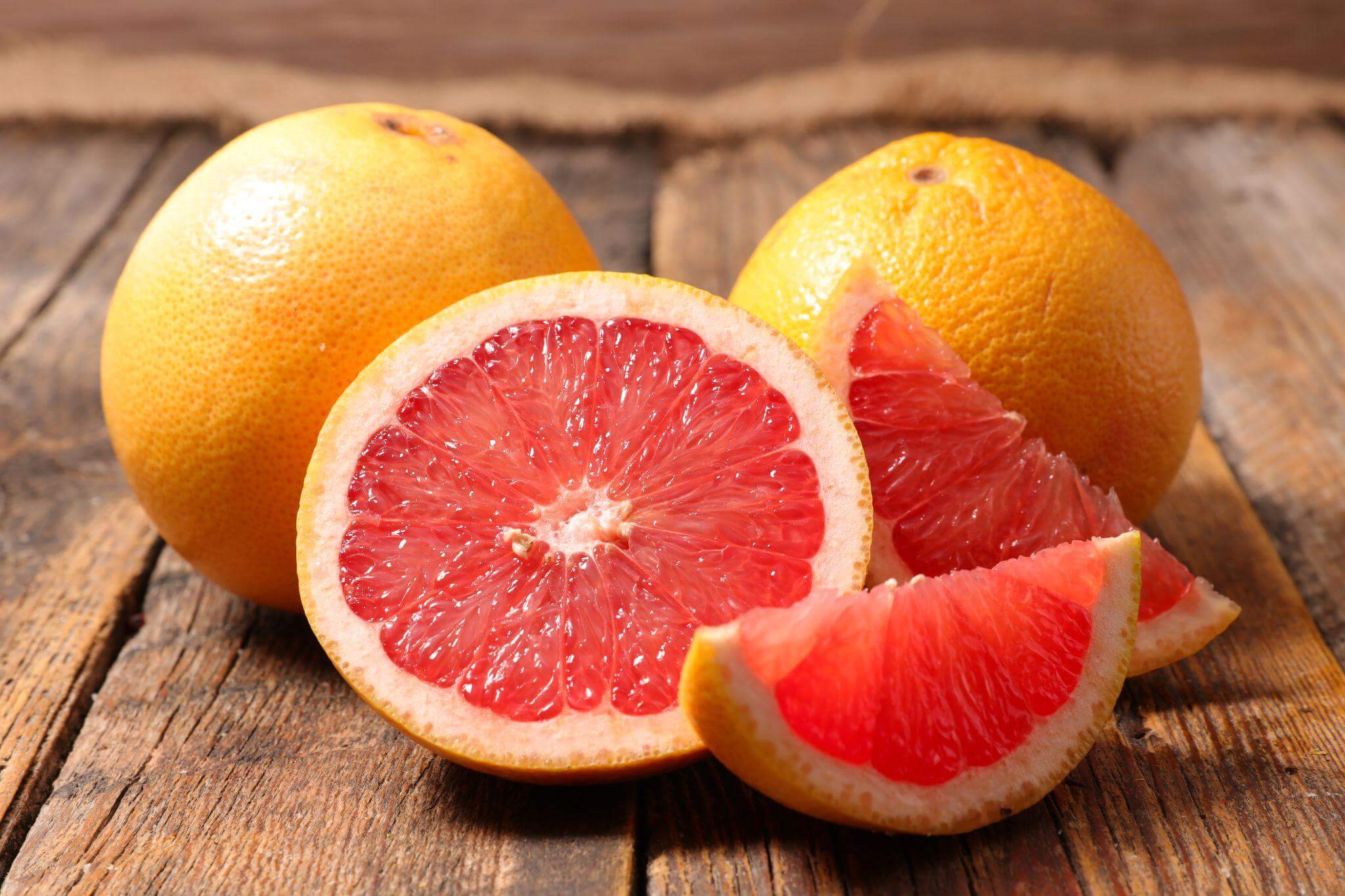

Some medications and supplements can interfere with levothyroxine. Let your doctor know about all the medications and over-the-counter products you take. Trained medical professionals can determine whether to prescribe levothyroxine to patients already taking other drugs.
If you are on levothyroxine, talk to your doctor before using any of these:
- Heartburn medications (antacids). Some antacids can interfere with levothyroxine absorption.
- Dietary fiber. Fiber can reduce the absorption of the drug in the stomach.
- Grapefruit. Grapefruit and grapefruit juice can hinder the absorption of many drugs, including levothyroxine.
- Soy. Like grapefruit, soy can prevent your body from absorbing adequate amounts of levothyroxine.
- Supplements containing iron and calcium. Iron and calcium bind to levothyroxine and can prevent the body from absorbing the medication.
These effects can often be managed by taking levothyroxine on an empty stomach or at a different time of day than your other medications.
What Should I Do If I Miss a Dose of Levothyroxine?
Do not double up on levothyroxine doses if you forget to take one; you can’t make up for the missed dose. If it’s almost time for your next dose, skip the one you forgot. If there’s still plenty of time before your next dose, take the dose you forgot as soon as possible.
Trying to make up for skipped doses can cause you to overdose on the medication.
What Should I Do If I Overdose on Levothyroxine?
The first step is to recognize that you’ve overdosed. Look out for these levothyroxine overdose symptoms:
- Cold skin
- Confusion
- Changes in pulse (fast or weak)
- Slurred speech
- Sudden onset of headache
- Loss of coordination
- Losing consciousness
- Changes in consciousness short of passing out
- Feeling disoriented
Some of levothyroxine’s common side effects may also indicate overdosing. If you realize you’ve overdosed, seek medical help immediately. Overdosing on levothyroxine is dangerous. If your doctor can’t provide emergency care, call the Poison Control Center at 1-800-222-1222.
Who Should Not Take Levothyroxine?
Levothyroxine is a synthetic version of a hormone you already have in your body. Most people are able to take the drug, but in some cases, a doctor may advise against it.
Though levothyroxine can have appetite suppression as a side effect, you should not take it for the purpose of weight loss. Other side effects can occur, some of which are dangerous and potentially fatal.
Avoid levothyroxine if you have:
- An adrenal problem
- Thyrotoxicosis, a thyroid disorder
- Heart attack symptoms like pain in the arms, jaw, shoulder, chest, etc.
You may not be a good candidate for treatment with levothyroxine if you have had one or more of the following conditions:
- Heart disease
- Kidney disease
- A low red blood cell count
- A thyroid nodule
- Pituitary gland problems
- Drug or food allergies
- Diabetes
In some cases, levothyroxine must be taken cautiously — a doctor will need to determine if the benefits of the drug justify its risks. For example, if you’ve had a heart attack, your doctor must ensure your heart has stabilized before prescribing levothyroxine.
If you have problems with your pituitary gland, your doctor must weigh carefully whether levothyroxine therapy is right for you. And thyroid therapy doesn’t work in people without well-functioning adrenal glands.
Be sure that all of your providers know your complete medical history, and report any unusual symptoms to your doctor.
Get the Lowest Price for Levothyroxine with BidRx

BidRx allows patients to create bids for the medications they need and let pharmacies compete to give them the lowest price.
In addition to giving patients access to the pharmacies that carry their drugs, BidRx also provides extensive information on the drugs, prices, discounts, and coupons.
Create a BidRx account today, create a bid, and select the medication you need for local pick-up or delivery.
Sign up here to start getting the lowest price on your levothyroxine and other medications.