Highlights
- COPD affects more than 15 million people in the U.S.
- The disease is incurable, but it can be managed with medication.
- There are many types and combinations of COPD medications. Your doctor can help you decide which is right for you.
- BidRx can help you find the lowest price for COPD medications.
What Is COPD?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD, is an umbrella term for a group of lung diseases, including emphysema and chronic bronchitis, that cause blockage of the airway and breathing problems.
COPD gets worse over time. In the U.S., 15 million people suffer from COPD, and many others don’t know they have the disease. Though there’s no cure for COPD, with the right medication, the condition is manageable.
About COPD Medications
If you have COPD, you have trouble drawing enough air into your lungs to oxygenate your blood adequately. You may have a persistent cough. You may also have trouble breathing and feel tightness around the chest.
Doctors believe that environmental toxins are at the root of COPD problems. Breathing in polluted air and smoking are common COPD causes and triggers.
There is no cure for COPD, and the damage it does to the airways is permanent. Medications aim to treat and alleviate the symptoms of the disease by reducing inflammation, slowing or stopping the progression of the disease, and helping you breathe easier.
Depending on the severity of your COPD, doctors prescribe medications from the following categories:
- Adrenergic bronchodilators
- Anticholinergic bronchodilators
- Combination bronchodilators
- Selective phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors
- Corticosteroids
- Methylxanthines
- Mucoactive drugs
- Antibiotics
- Biologic drugs
- Cancer medications for COPD
Here’s what you need to know about each commonly prescribed type of COPD medication.
Adrenergic Bronchodilators
Bronchodilators are available in both short-acting and long-acting formulations. They act directly on the receptors of the bronchial smooth muscles, relaxing the muscles. As the muscles relax, the bronchi dilate, allowing more air to flow through. Bronchodilators require direct contact with the muscles of the airways. They are available as inhalers or nebulizers.
Short-acting bronchodilators offer relief as needed. If you have a COPD attack, you can use them to cut the attack short and regain your breath.
Long-acting bronchodilators are daily, or maintenance, medications. Patients take these twice a day as part of standalone and adjunct therapies.
Your doctor may describe different bronchodilators for acute COPD, COPD maintenance, and COPD treatment. All bronchodilators require a prescription.
This class of bronchodilators includes:
- Albuterol (Albuterol Inhalation Solution)
- Levalbuterol (Xopenex, Xopenex Concentrate)
- Formoterol (Atock, Foradil, Fostair)
- Arformoterol (Brovana)
- Olodaterol (Respimat, Striverdi)
- Pirbuterol (Maxair)
- Salmeterol (Serevent, Diskus)
- Metaproterenol (Alupent)
- Indacaterol (Arcapta Neohaler)
Warnings and Contraindications — Adrenergic Bronchodilators
Do not take short- or long-acting bronchodilators if you are allergic to any of their components. If you notice signs of an allergic reaction after you take a bronchodilator, seek medical attention immediately.
Before your doctor prescribes an adrenergic bronchodilator, talk to him or her about your health conditions, especially if you have:
- Diabetes
- Thyroid disorders
- High blood pressure
- Heart disease
- Seizures
Very young children (under four years of age) should not take bronchodilators. If you overdose by mistake, seek medical help immediately. Overdosing on adrenergic bronchodilators can be fatal.
Side Effects — Adrenergic Bronchodilators
Adrenergic bronchodilators are potent drugs. To some COPD sufferers, they can be lifesavers. Their side effects are also significant.
If you experience any of these side effects, seek medical help immediately:
- Breathing problems, choking or wheezing after taking a puff
- Irregular heartbeats
- Asthma symptoms that go from bad to worse
- Constipation
- Severe thirst
- Muscle weakness
- Frequent urination
Other severe side effects of this class of drugs can include:
- Tremors
- Sore throat
- Dizziness
- Chest pain
- Vomiting
Drug Interactions — Adrenergic Bronchodilators
Bronchodilators can interact with many drugs:
- Antidepressants
- Diuretics
- Heart medications
- Other COPD medications taken through inhalers
- Vitamins, herbal products, and dietary supplements
Anticholinergic Bronchodilators

These drugs act on the neurotransmitter acetylcholine to override the nerve reflexes that constrict the airways. Like all other bronchodilators, anticholinergic bronchodilators are prescription-only medications.
- Tiotropium (Spiriva)
- Umeclidinium (Incruse, Ellipta)
- Aclidinium (Tudorza, Pressair)
- Ipratropium (Atrovent)
- Glycopyrrolate (Cuvposa, Dartisla, Robinul)
- Revefenacin (Yupelri)
Warnings and Contraindications — Anticholinergic Bronchodilators
Anticholinergic bronchodilators like revefenacin are not suitable for emergency use. For bronchospasm attacks, use a fast-acting bronchodilator.
If you feel that your bronchodilator stops working or you exhibit allergic symptoms, contact your doctor immediately.
Before starting treatment with anticholinergic bronchodilators, tell your doctors if you have any of these conditions:
- Liver disease
- Benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH)
- Glaucoma
- Urination problems
Never give anticholinergic bronchodilators to children. If you overdose by accident, seek medical help.
Symptoms that might indicate on overdose include:
- Light-headedness
- Vomiting
- Nausea
- Problems urinating
- Vision problems
Side Effects — Anticholinergic Bronchodilators
If you notice that your tongue or face swells after taking anticholinergic bronchodilators, seek medical help immediately.
These drugs are potent and may produce many severe side effects that can include:
- Breathing problems and wheezing after you take the drug
- Vision problems including tunnel vision, blurred vision, eye pain, irritation, seeing halos around lights
- Difficulty or pain while urinating
- Weak urine stream and incomplete emptying of the bladder
Some of the less-severe and more common side effects of the drugs are:
- Runny and stuffy nose
- Back pain
- Coughing
- Sore throat
- Headache
Anticholinergic bronchodilators may cause other side effects not listed here. If you experience unusual symptoms after using your medication, speak with your doctor right away.
Drug Interactions — Anticholinergic Bronchodilators
Because they are potent drugs that impact vital neurotransmitters, anticholinergic bronchodilators may interact with many other drugs, vitamins, and supplements.
These prescription and over-the-counter products can include:
- Allergy drugs like Benadryl
- Drugs that treat irritable bowel syndrome and other digestive ailments
- Other bronchodilators
- Depression medication
- Medication used to treat mental disorders
- Parkinson’s disease drugs
- Asthma medications
This list is not complete. Tell your doctor about any drugs you take before starting treatment with anticholinergic bronchodilators.
Combination Bronchodilators
Some patients whose COPD does not respond to treatment may need a combination of medications to relieve their symptoms. Doctors sometimes prescribe combination medications containing two active drugs, or even triple combinations of two long-acting bronchodilators and a corticosteroid.
According to a 2018 study, triple therapy involving three COPD medications results in better lung function and fewer COPD flare-ups in patients.
Combination therapy entails some risks. Patients are more likely to develop pneumonia with three drugs than with two.
The two-drug therapy is, therefore, the safer approach to controlling COPD and improving lung function. All combination bronchodilators are prescription-only medications.
These are the most common combination bronchodilators:
- Fluticasone/umeclidinium/vilanterol (Trelegy Ellipta)
- Budesonide/formoterol (Breyna, Symbicort)
- Fluticasone/vilanterol (Breo Ellipta)
- Umeclidinium/vilanterol (Anaro Ellipta)
- Olodaterol/tiotropium (Stiolto Respimat)
- Aclidinium/forrmoterol (Duaklir Pressair)
- Budesonide/formoterol/glycopyrrolate (Breztri Aeropshere)
- Formoterol/glycopyrrolate (Bevespi Aeropshere)
Warnings and Contraindications — Combination Bronchodilators
Combination bronchodilators are highly potent medications, but many of these medications are not fast-acting enough to serve as rescue solutions for bronchospasm attacks.
Avoid these medications if you are allergic to milk proteins or their components. You can develop an allergy to a compound after prolonged exposure. If you notice signs of an allergic reaction when using your medication, seek medical attention immediately.
You shouldn’t take combination bronchodilators if you have:
- An enlarged prostate
- Problems with your immune system or thyroid
- Diabetes
- Liver disease
- Heart disease
- Glaucoma
- Osteoporosis
People younger than 18 years should not use combination bronchodilators. Breastfeeding and pregnant women should also avoid these medications.
Side Effects — Combination Bronchodilators
If you take an overdose of these drugs, you may experience:
- Accelerated heart rate
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Shakiness
You may experience some side effects even when you use combination bronchodilators according to your doctor’s recommendation.
Common side effects include:
- Sores in your mouth
- Joint pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Headaches
- Back pain
- Difficult urination
- Lung infections
Triple-therapy drugs are more likely to cause lung infections than two-drug combinations. The more severe side effects of this class of drugs include:
- Fast heartbeat
- Chest pain
- Tunnel vision
- Eye pain
- Exhaustion
- Difficult urination
- Difficulty breathing
- Fever, chills, and lung infection
- Dry mouth
- Thirst
Drug Interactions — Combination Bronchodilators
These drugs may interact with many other drugs, supplements, vitamins, herbal products, and foods.
Tell your doctor if you’re using any of the following medications:
- Antiviral or antifungal drugs
- Benadryl or other allergy and/or cold medications
- Medications for stomach problems, motion sickness, or irritable bowel syndrome
- Atropine
- Other bronchodilators
- Medication for Parkinson’s disease
Drug interaction lists are never complete. If you’re taking another drug for a different condition, you may be at risk. Be sure to keep your providers up to date on all of the drugs and supplements you’re taking.
Corticosteroids
Autoimmune inflammation is one of the causes of COPD. Corticosteroids can reduce inflammation and help alleviate COPD symptoms.
Some corticosteroids come in an inhalable form. Others are available as pills, liquids, or injections.
Corticosteroids are potent medications with potentially severe side effects. These drugs are only available by prescription.
Corticosteroids prescribed for COPD include:
- Fluticasone (Flovent Diskus, Flovent, Flovent HFA, and others)
- Budesonide (Uceris, Ortikos, Entocort EC)
- Prednisone (Rayos)
Warnings and Contraindications — Corticosteroids
Steroids modulate your immune system, so they can weaken it and predispose you to various infections.
Stay away from infected people, and do not get vaccinated while you are on corticosteroids.
Be sure your doctor has a complete list of all your medical conditions and medications. Seek medical help immediately if you have an allergic reaction to a corticosteroid medication.
Corticosteroids may not be an option for you if you have:
- Glaucoma
- Liver disease
- Tuberculosis
- A herpes infection in your eyes
- A weak immune system
- A parasitic infection
- Osteoporosis
Side Effects— Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids can cause many common side effects, including:
- Insomnia
- Mood swings
- Acne
- Headache
- Sweating
- Dry skin
- Weight gain
- Increased appetite
Their more-severe but less-common side effects can include:
- Eye pain
- Muscle weakness
- Severe depression
- Tarry and bloody stools
- High blood pressure
- Seizures
- Pancreatitis
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
Seek medical help immediately if you experience any of these severe side effects.
Drug Interactions — Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids can interact with many drugs. Vitamins, supplements, and herbal products are also sources of risk. Tell your doctor about all the medications and supplements you take before going on corticosteroids.
Some, but not all, of the drugs that interact with corticosteroids are:
- St. John’s wort
- Digoxin
- Cyclosporine
- Antibiotics like clarithromycin
- Antifungal medications like ketoconazole
- Blood thinners
- Birth control pills
- Anything that affects your hormone levels
- Hepatitis C medications
- Diuretics
- Seizure medications
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like aspirin
Selective Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitors
Roflumilast is the only phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor doctors use to treat COPD. Available under the brand name Daliresp, this drug targets the root of the COPD problem, inflammation in the lungs.
If your doctor prescribes this drug, you probably have severe COPD. The treatment goal is to prevent the worsening of COPD symptoms. The drug comes in pill form taken orally once a day.
Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors are not bronchodilators or rescue medications. They won’t abort a COPD attack.
Warnings and Contraindications — Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitors
If you have liver disease or mental problems, including depression and suicidal thoughts, Roflumilast is not a suitable option for you. Tell your doctor about your mental and physical health conditions to avoid the severe consequences these drugs can produce.
Do not take Roflumilast if you are allergic to it. Note that with repeated exposure, you may develop an allergy to a drug you used to tolerate well. If you notice allergic reactions at any time, seek medical attention immediately.
The drug can change your mood and lead to suicidal thoughts while you’re taking it. Have your caretakers and doctors monitor your treatment regularly.
Pregnant women and children should not take this drug.
Side Effects — Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitors
Roflumilast’s common side effects include:
- Nausea
- Loss of appetite
- Digestive problems
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Flu-like symptoms
- Sleep problems
- Back pain
- Some weight loss
Severe side effects can include:
- Severe and sudden weight loss
- Painful urination
- Tremors
If you experience any of the effects on this list, seek medical help immediately.
Drug Interactions — Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitors
Tell your doctor about all medications, supplements, and vitamins you use. Roflumilast can interact with many other drugs, supplements, and vitamins.
Methylxanthines
Methylxanthines are a class of drugs used to treat COPD patients who do not respond to bronchodilators. Your doctor may prescribe a methylxanthine called theophylline to augment your bronchodilator or corticosteroid treatment.
At lower doses, theophylline protects the airways, reduces inflammation, and modulates immune responses. To exert a bronchodilator effect, doctors must prescribe higher doses. At higher doses, methylxanthines like theophylline can be toxic.
Given their toxicity risk, it is unsurprising that methylxanthines are all prescription-only medications.
Methylxanthines used to treat COPD include:
- Theophylline (Elixophillin, Respbid, Theo-24, and others)
- Aminophylline (Phyllocontin, Truphylline)
- Dyphylline (Dilor-200, Dilor-400, Dylix , and others )
Warnings and Contraindications — Methylxanthines
In addition to COPD, doctors use theophylline to treat other breathing problems like bronchitis, asthma, and emphysema.
The drug can be toxic in higher dosages, so never take more than your doctor prescribes.
Tell your doctor if you drink alcohol, smoke, or have recently quit smoking. You are not a good candidate for treatment with methylxanthines if you have:
- Kidney disease
- Thyroid problems
- Gastric ulcer
- Liver disease
- Heart disease
- Sepsis
- Seizures
Before prescribing methylxanthines, your doctor should also know whether you have a fever or are pregnant or breastfeeding.
It’s extremely important never to take more methylxanthine than prescribed. An overdose of these drugs can cause seizures resulting in permanent brain damage or death.
Side Effects — Methylxanthines
The common side effects of this class of drugs include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Irritability and restlessness
- Sweating
- Trouble sleeping
- Headaches
Methylxanthines can cause severe side effects, like:
- Seizures
- Rapid heartbeat
- Severe vomiting
- Fever
- Severe headache
- Spiked blood sugar
- Constipation
- Muscle weakness
Seek medical help if you experience any of these side effects.
Drug Interactions — Methylxanthines
Many drugs, herbal supplements, and vitamins can interact with methylxanthines. According to Drugs.com, St. John’s wort is an herbal product that can affect the levels of theophylline in your blood.
Always talk to your doctor about the medications you take before beginning treatment with a methylxanthine.
Mucoactive Drugs
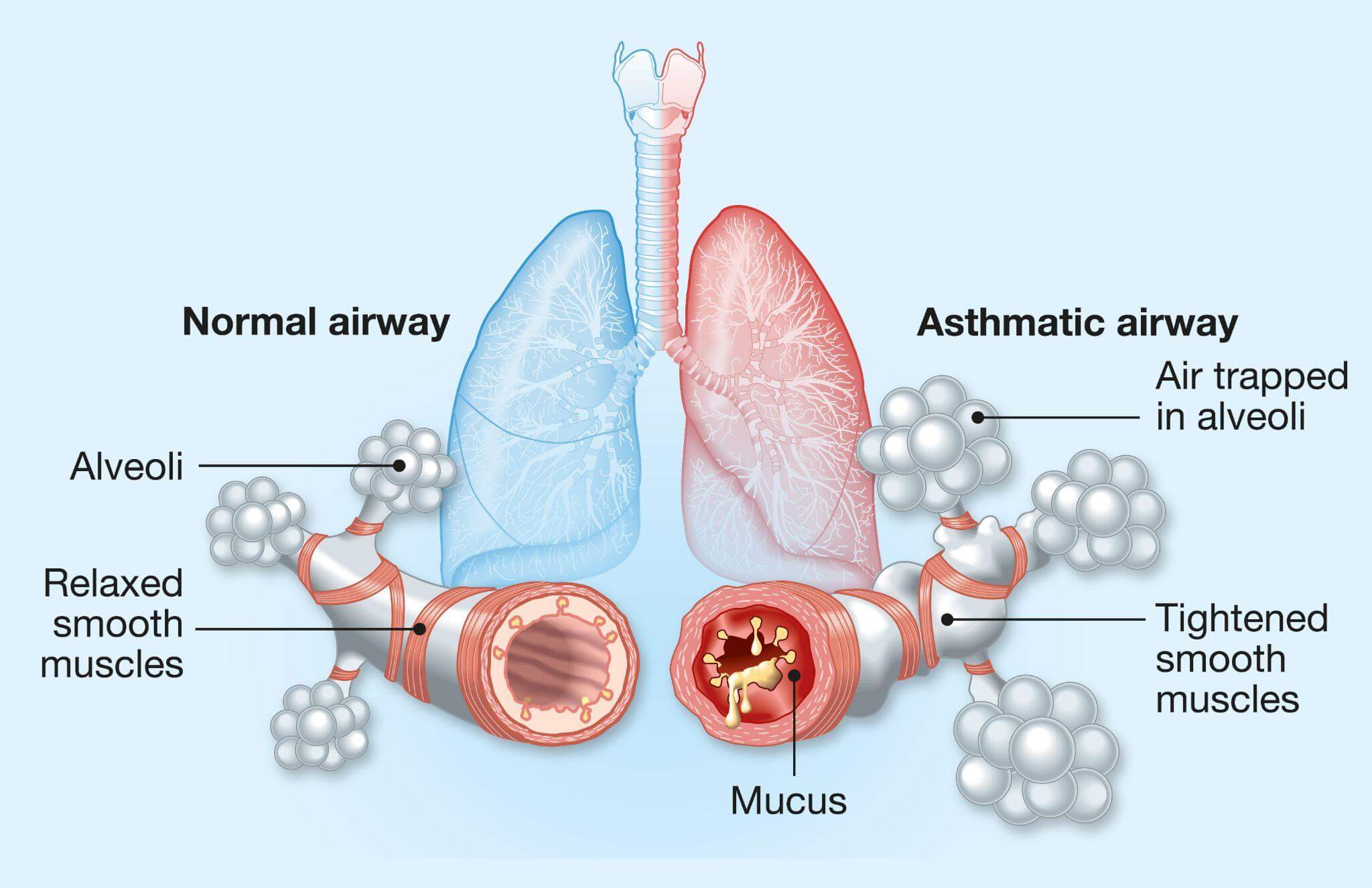
A 2019 study found that mucoactive drugs could alleviate the symptoms of COPD and reduce the intensity of flare-ups. They achieve these effects by reducing the buildup of mucus in the lungs COPD causes.
In addition to helping the lungs eliminate mucus, some mucoactive drugs also fight inflammation, acting as antioxidants.
Mucolytic drugs are prescription only.
- Cabocysteine (Availnex)
- Erdosteine (Erdomed, Erdotin, others)
- N-acetylcisteine (Acys-5, Acetylcisteine Solution)
Warnings and Contraindications — Mucoactive Drugs
Mucoactive drugs like acetylcysteine can limit liver damage in patients who take acetaminophen-based drugs, like Tylenol. Do not attempt to treat yourself with acetylcysteine if you suspect you may have overdosed on acetaminophen. Let your doctor set your treatment.
Do not use mucoactive drugs if you are allergic to any of their components. Tell your doctors about your health conditions before they prescribe treatment.
Mucoactive drugs may not be suitable for COPD patients also suffering from:
- Kidney disease
- High blood pressure
- Heart failure
- Stomach ulcer
- Stomach bleeding
Pregnant and breastfeeding women should not take these drugs without their doctors’ recommendation.
Side Effects — Mucoactive Drugs
The side effects of mucoactive drugs range from common to severe. Common side effects include:
- Fever
- Nausea
- Rash
- Digestive problems
Some possible severe side effects are:
- Severe vomiting
- Stomach bleeding
- Vomiting a coffee grounds-like material
- Jaundice
- Clay-colored stools
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
Mucoactive drugs may have other side effects not listed here.
Drug Interactions — Mucoactive Drugs
A variety of vitamins, supplements, herbal products, and drugs can interact with mucoactive medications. Tell your doctor about all drugs or supplements you take to avoid interactions and save yourself from unnecessary suffering.
Biologic Drugs
A higher-than-normal count of white blood cells called eosinophils can cause inflammation in the body. Because inflammation contributes to COPD, medications that treat inflammation can improve COPD symptoms.
Biologic drugs give doctors the tools to interfere with the inflammation process. Eosinophilia can also cause asthma, and several biologic drugs used to treat asthma may work for COPD as well.
Biologic drugs are advanced medications representing the cutting edge of science because they’re created from living cells.
Drugs in this class are all prescription-based and include:
- Mepolizumab (Nucala Prefilled Syringe, Nucala)
- Benralizumab (Fasenra)
- Reslizumab (Cinqair)
- Dupilumab (Dupixent)
Warnings and Contraindications — Biologic Drugs
Tell your doctor if you have any of these conditions:
- Asthma treated with steroids
- Parasite infections like tapeworm
- Shingles
Children should not take biologic drugs for COPD.
Side Effects — Biologic Drugs
Some common side effects of biologic drugs include:
- Back pain
- Exhaustion
- Headache
- Burning and itching at the site of the infection
Serious side effects can include:
- Unusual pain
- Tingling in the body
- Skin rash
- Blistering
Drug Interactions — Biologic drugs
Biologic drugs can interact with many other drugs, supplements, and vitamins. Fexinidazole is one example of a drug that can interact with these medications, but there are others. Tell your providers about all the medications and supplements you take.
Antibiotics

Some antibiotics may reduce the frequency and intensity of COPD flare-ups. Antibiotics are all prescription-based medicines. The two antibiotics doctors may prescribe for COPD are azithromycin (Azasite, Zithromax, Zmax, and others) and erythromycin (EryPed 200 EryPed 400, Ery-Tab, and others).
Warnings and Contraindications — Antibiotics
The regular use of antibiotics may lead to antibiotic resistance. The long-term use of these drugs may lead to many as yet unknown side effects.
Side Effects — Antibiotics
Azithromycin use can result in hearing loss. Antibiotics in general can have a multitude of other side effects like:
- Diarrhea
- Headaches
- Stomach pain
- Vomiting
- Liver problems
- Digestive problems
- Severe pain
- Bloody stool
If you experience severe side effects, call your doctor immediately.
Drug Interactions — Antibiotics
These antibiotics may interact with digoxin, warfarin, and clarithromycin, among others. Always talk to your doctor about the medications you take. All drugs can interact with various supplements, herbal products, and vitamins.
Vaccines and Cancer Medications
Researchers believe that influenza vaccines may limit COPD flare-ups. And they can certainly help with infections that may aggravate COPD.
The cancer drug tyrphostin AG825 may also help lower the inflammation responsible for COPD.
Dealing With COPD at Home
If you’re a smoker, quit all smoking as soon as possible. Stay away from areas where others smoke. Quitting smoking may not be easy, but you must do it to slow the damage COPD does to your lungs.
Respiratory infections and air pollution may cause flare-ups in your COPD. Try to avoid these triggers.
COPD medications are all prescription-based, with strong effects and side effects. Overdosing on these drugs can be dangerous. Always follow medication directions exactly.
It is always better to err on the side of caution if you are unsure how to take your COPD medications or forget to take them. Don’t hesitate to contact your healthcare provider if you have any questions.
Find the Lowest Price for COPD Medications

Join BidRX and find the best price for COPD medications by letting pharmacies compete to give you the lowest possible price.
Simply sign up, create a bid, and let pharmacies come to you with their best prices for your medications. You can then compare prices and choose your offer.
Find your COPD medicines on the medication page and place your bid today!
