Highlights
- Chronic kidney disease is a silent killer affecting one in seven adults in the U.S.
- Chronic kidney disease medications can slow the progression of the disease and reduce its symptoms.
- Treatment for CKD usually consists of treating the conditions that cause kidney failure.
- Let BidRx help you find the best price for your CKD medications.
One in seven adults in the U.S. suffers from chronic kidney disease. The tragedy is that nine out of ten CKD sufferers don’t know they have the condition until the disease has done its damage. CKD is incurable, but chronic kidney disease medications can slow its progression and improve the daily lives of sufferers.
What Is Chronic Kidney Disease?
Chronic kidney disease is a condition that can develop as a result of high blood pressure, diabetes, or high cholesterol. Hereditary factors also raise the risk of CKD, as do smoking, heart disease, and obesity.
Doctors can’t cure CKD, but they can prescribe medication that can alleviate symptoms and slow the progression of the disease. Early CKD is difficult to detect and diagnose. Often, patients only receive treatment when their CKD reaches an advanced stage. End-stage kidney disease requires a kidney transplant or dialysis.
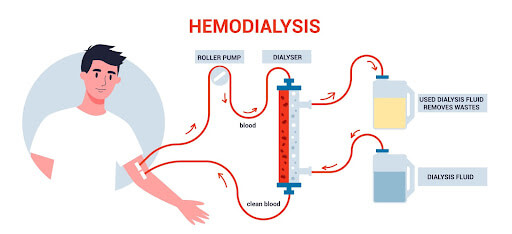
Dialysis is a treatment for end-stage kidney disease.
About Chronic Kidney Disease Medications
CKD medications offer few options for direct treatment. Doctors can often treat the conditions that cause CKD, however, with drug-based treatments that focus on conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol.
CKD treatments require precision and strict adherence to your doctor’s indications. To devise dosage and dosage intervals, doctors must consider the patient’s glomerular filtration rate (GFR). GFR is the chief indicator of kidney function, and varies from patient to patient.
Doctors may not be able to prescribe some chronic kidney disease medications to patients with severe kidney impairment.
The main classes of medications used to treat chronic kidney disease are:
- Aldosterone receptor antagonists
- Sglt-2 inhibitors
- Hypertension medications
- ACE inhibitors
- Angiotensin-2 receptor blockers
- Statins (cholesterol medications)
- High potassium-level medications
- Sodium zirconium cyclosilicate
- Diuretics
- Anemia medications
- Hormone injections
- Vitamins
- Medications for bone problems
- Phosphate binders
- Vitamins
- Glomerulonephritis medications
- Steroids
- Immunosuppressants
Aldosterone Receptor Antagonists
Finerenone is an aldosterone receptor antagonist doctors prescribe for chronic kidney disease. Finerenone is a prescription-only medication used to reduce the risks of CKD in patients suffering from diabetes mellitus type 2.
Finerenone is used to reduce the risk of:
- Sudden loss of kidney function
- Heart failure
- Heart attack
- Hospitalization for heart disease
This medication may also slow the progression of CKD. The drug is an oral tablet available under the brand name Kerendia, which is prescribed for other medical conditions, as well.
Warnings and Contraindications — Aldosterone Receptor Antagonists
Patients with adrenal gland problems should not take finerenone. If you are allergic to this medication, tell your doctor about it. If you develop allergic symptoms after taking it, seek medical attention immediately.
You should also avoid finerenone if you have high potassium levels in your blood or severe liver disease. Pregnant women should exercise caution with this drug. No one under 18 should take finerenone.
Side Effects — Aldosterone Receptor Antagonists
Finerenone’s side effects range from mild to severe. The common side effects of the drug include:
- Low blood pressure
- Low sodium levels
- High potassium
Severe side effects may include:
- Chest pain, irregular heartbeats, and weakness stemming from high blood potassium
- Headaches, weakness, confusion, and memory problems due to low sodium
This side effect list is not complete; check with your provider if you experience any new or unusual symptoms while taking this medication.
Drug Interactions — Aldosterone Receptor Antagonists
Finerenone may interact with many other drugs. Tell your doctor about all other medications you take. Your treatment may change if you take:
- Nefazodone
- Antibiotics like clarithromycin.
- Antifungal drugs like ketokonazole
- Hepatitis C or HIV medications
The list is not complete; aldosterone receptor antagonists may interact with other drugs, so be sure your doctor knows about all medications and supplements you’re taking.
SGLT-2 Inhibitors
These medications are FDA approved to treat hypertension and heart failure in people with type 2 diabetes. They work by helping the body eliminate glucose through urination.
Dapagliflozin (Farxiga) is an SGLT-2 inhibitor that is also effective at slowing the progression of chronic kidney disease. It’s often prescribed for people with CKD, both those who do and those who do not have diabetes.
Contraindications — Dapagliflozin
Avoid all SGLT-2 inhibitors if you have type 1 diabetes. These medications are also not appropriate for people who already have moderate to severe kidney damage.
You should not take drugs in this class if you are allergic to them. The drug may not be safe for people younger than 18.
Also, avoid SGLT-2 inhibitors if you have:
- Liver problems
- A urinary tract infection
- Pancreatitis
- A change in your diet
- A habit of binge drinking
Side Effects — Dapagliflozin
SGLT-2 inhibitors can cause dehydration leading to sudden kidney injury. Dehydration can also make you feel weak, dizzy, and lightheaded.
People who take diuretics to lower their blood pressure are at an increased risk of dehydration when taking SGLT-2 Inhibitors.
If you have kidney problems, are older than 65, or do not include enough salt in your diet, you are also at an increased risk of dehydration from SGLT-2 inhibitors.
In people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, SGLT-2 inhibitors can cause a condition called ketoacidosis. Ketoacidosis may be lethal.
Other severe side effects of dapagliflozin include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Difficulty breathing
- Abdominal pain
- Low blood sugar
- Urinary tract infections
- Necrotizing fasciitis, a disease that may also be lethal.
The more common side effects of these drugs include:
- Sore throat
- Stuffy nose
- Changes in urination habits
- Yeast infections of the vagina or penis
Drug Interactions — SGLT-2 Inhibitors
SGLT-2 inhibitors may cause dehydration when combined with diuretics. Dapagliflozin can interact with 325 medications, among them aspirin, paracetamol (acetaminophen), and vitamin C. Be sure all of your providers have an up-to-date list of all medications and supplements you take.
Angiotensin-converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors
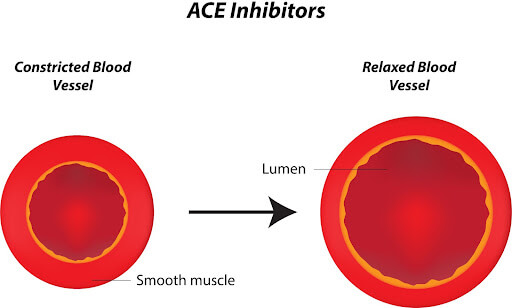
ACE inhibitors treat high blood pressure as well as some kidney diseases. They help with kidney disease by lowering blood pressure.
All ACE inhibitors target an enzyme that narrows the blood vessels and helps the body release hormones like aldosterone and norepinephrine. This enzyme, angiotensin II, and the hormones it helps release, can all contribute to the narrowing of blood vessels and increase blood pressure.
By blocking this enzyme, ACE inhibitors lower blood pressure, kidney pressure, and urine production.
ACE inhibitors are generally safe to take and well-tolerated. Some of their side effects may be severe, however. All ACE inhibitors are prescription-only medications.
- Lisinopril (Zestril, Prinivil, and others)
- Ramipril (Altace)
- Perindopril (Aceon)
- Enalapril (Vasotec, Epaned)
- Benazepril (Lotensin)
- Captopril (Capoten)
- Tandolapril (Mavik)
- Fosinopril (Monopril)
- Moexipril (Univasc)
- Quinapril (Accupril)
In addition to kidney disease and high blood pressure, doctors may also prescribe ACE inhibitors for:
- Heart attack
- Heart failure
- Coronary artery disease
- Left ventricular dysfunction
Warnings and Contraindications — ACE Inhibitors
ACE inhibitors are strong medications with profound effects on the body. Always heed your doctor’s prescription and never exceed the prescribed doses. Avoid taking ACE inhibitors if you are allergic to any of them. If you notice allergic symptoms, seek medical help immediately.
Talk to your doctors about the health problems and conditions you have. You may not be able to take ACE inhibitors if you have had:
- Heart disease
- Liver disease
- Kidney disease
- An organ transplant
Pregnant women and children should not take ACE inhibitors.
Side Effects — ACE Inhibitors
ACE inhibitors can cause a wide range of side effects. In some patients, these side effects may grow so troublesome that they must discontinue using the medication. The common side effects of ACE inhibitors include:
- Dizziness
- Blurred vision
- Dry mouth
- Fatigue
- Sweating
- Headaches
- High levels of potassium and creatinine in the blood
- Low blood pressure
- Dry cough
These drugs can also cause more severe side effects, such as:
- Severe, life-threatening allergic reactions
- In pregnant women, miscarriage or harm to the kidneys of the fetus
- Angioedema, or swelling of the tongue and throat
Angioedema is more likely to occur in patients who smoke or belong to the African-American ethnicity.
Drug Interactions — ACE Inhibitors
ACE inhibitors can interact with many drugs. The following are the most common and well-known interactions, but the list is incomplete.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Oral diabetes medications and insulin
- Other medications used to manage blood pressure
- Diuretics
- Lithium
- Gold injections for arthritis
Many different types of ACE inhibitors exist. Their drug interactions and side effect profiles may differ.
To patients who cannot take ACE inhibitors due to their disruptive side effects, doctors may prescribe angiotensin-2 receptor blockers (ARBs).
Angiotensin-2 Receptor Blockers (ARBs)
Like ACE inhibitors, ARBs target angiotensin-2. By blocking this enzyme, these drugs relax and dilate the blood vessels, reducing blood pressure and urine production.
ARBs may be a solution for patients who can’t take ACE inhibitors. Doctors use angiotensin-2 receptor blockers to treat chronic kidney disease, diabetic kidney failure, and heart failure.
Like ACE inhibitors, angiotensin-2 receptor blockers are prescription-only medications.
- Eprosartan
- Losartan (Cozaar)
- Telmisartan (Micardis)
- Valsartan (Diovan)
- Olmesartan (Benicar)
- Irbesartan (Avapro)
- Candesartan (Atacand)
- Azilsartan (Edarbi)
Warnings and Contraindications — Angiotensin-2 Receptor Blockers
Pregnant women or women planning to become pregnant should avoid taking drugs in this class.
People who can’t take ACE inhibitors because of low blood pressure, kidney failure, or elevated potassium should also avoid ARBs.
Side Effects — Angiotensin-2 Receptor Blockers
Many of the common side effects of ARBs coincide with those of other medications that lower blood pressure. They can include:
- Dizziness
- Lightheadedness
- Weakness
- Swelling of the face, tongue, or lips
- Trouble breathing
Breathing problems and facial swelling can be symptoms of an allergic reaction. Seek medical attention immediately if you experience these side effects.
ARBs can also affect kidney function and cause potassium buildup in the blood.
Drug Interactions — Angiotensin-2 Receptor Blockers
ARBs can interact with:
- NSAIDs
- Nasal decongestants
- Medications that affect blood pressure
Always talk to your doctor about all medications and supplements you take.
Statins
Doctors use statins to lower total and LDL cholesterol levels. Because high cholesterol can cause chronic kidney disease, lowering cholesterol levels can also treat CKD.
Statins work by blocking an enzyme called HMG-CoA reductase. The body uses HMG-CoA reductase to make mevalonate, a compound that acts as raw material for the body’s cholesterol production.
In addition to lowering cholesterol production at its source, statins also increase the number of cholesterol receptors in the liver, allowing it to break down more LDL cholesterol.
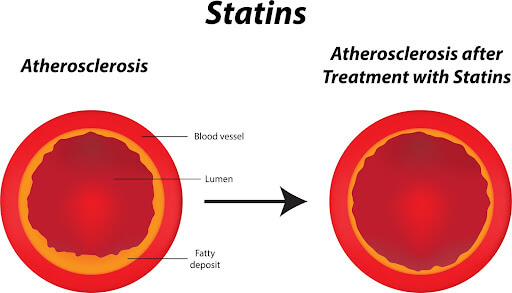
Low cholesterol levels also reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Statins are prescription-only medications. Drugs in this class include:
- Atorvastatin (Lipitor)
- Fluvastatin (Lescol)
- Lovastatin (Altoprev)
- Pitavastatin (Zypitamag, Livalo)
- Pravastatin (Pravachol)
- Rosuvastatin (Crestor)
- Simvastatin (Zocor)
Warnings and Contraindications — Statins
If you are a heavy alcohol drinker, you shouldn’t take statins. People with liver disease should also avoid these medications. Statins can cause severe muscle-related side effects, so doctors may not prescribe them to people with a history of muscle disease.
Side Effects — Statins
The common side effects of these medications include:
- Constipation
- Bloating
- Headaches
- Muscle pain and weakness
- Lower back pain
- Sleep disturbances
- Stuffy nose
- Difficult urination
- Sweating
Statins can cause some severe side effects as well. Never exceed the dosage your doctor prescribes, and always take your medications according to your doctor’s directions.
The more-severe side effects of statins can include:
- Liver disease and jaundice
- The destruction of muscle cells
- Memory loss
- Confusion
- Neurological problems
- Type 2 diabetes
Drug Interactions — Statins
Statins can interact with many drugs, herbal supplements, and vitamins. People who drink alcohol or take HIV antiviral medications, cyclosporine, or itraconazole, are more likely to experience side effects.
Statins can also interact with some antibiotics and antifungal medications.
Potassium Binders
Potassium binders are drugs that treat high blood potassium levels, a common problem for people with chronic kidney disease. They work by binding the excess potassium in the gut before it reaches the bloodstream and eliminating it through bowel movements.
There are many potassium binders, but the two used most often for CKD are sodium zirconium cyclosilicate (brand name Lokelma) and patiromer (brand name Veltassa). Both are available only by prescription.
Warning and Contraindications – Potassium Binders
Sodium Zirconium Cyclosilicate
CKD patients on dialysis should not take potassium binders on dialysis days. Drugs like sodium zirconium cyclosilicate may interfere with X-rays as they show up on the images.
If you have hard stools and problems with your bowel movements, you may not be a good candidate for this treatment.
If you notice allergic reactions to the drug, seek medical attention immediately.
Patiromer
Patiromer may not be an appropriate choice for people who have severe constipation or bowel obstruction or those who have had recent bowel surgery.
Side Effects – Potassium Binders
Sodium zirconium cyclosilicate
The body seems to tolerate this medication well. However, the most common side effect is the potential for fluid retention, leading to the swelling of extremities like the hands, ankles, and feet. Chronic kidney disease already causes fluid retention and swelling, and sodium zirconium cyclosilicate may exacerbate the problem.
Patiromer
The common side effects of this medication include:
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Stomach pain
- Nausea
- Gas
More serious side effects of patiromer can include:
- Nystagmus (involuntary movements of the eyes)
- Seizure
- Muscle pain or weakness
- Numbness
- Fatigue
To counterbalance the negative effects of potassium binders on fluid retention, doctors may prescribe higher doses of diuretics. They may also choose to monitor your blood potassium levels while under treatment. If your blood potassium level drops too much, your doctor may adjust your dose.
Drug Interactions – Potassium Binders
Sodium Zirconium Cyclosilicate
There are 17 drugs that are known to interact with sodium zirconium cyclosilicate, including some common ones, such as furosemide and atorvastatin, as well as some antifungals and antivirals. This drug may also interact with diuretics and can affect the absorption of other oral medications.
Patiromer
A total of 90 drugs from many classes are known to interact with patiromer. This medication can interfere with absorption of other medications, so your doctor will probably recommend taking it at least three hours before or after other medications. Patiromer can also lower magnesium levels in the blood, so you will probably be monitored regularly for signs of magnesium deficiency and possibly prescribed a magnesium supplement.
Diuretics
Since the kidneys of those suffering from CKD don’t work as well as they should, people with the disease can have trouble eliminating fluids from the body. The excess fluids can build up in the ankles, hands, and feet, leading to swelling.
Doctors may prescribe diuretics to help the body eliminate the fluids. Diuretics are drugs that make you urinate more. Overuse can be dangerous, as one of their side effects is dehydration.
Diuretics are prescription-only medications. Always take diuretics exactly as prescribed; dehydration can be life-threatening.
For CKD patients, doctors may recommend potent diuretics known as loop diuretics. Drugs in this class include:
- Bumetanide (Bumex)
- Ethacrynic acid (Edecrin, Sodium Edecrin)
- Furosemide (Lasix, Lo-Aqua, diaqua-2)
- Torsemide (Demadex)
Warnings and Contraindications – Diuretics
Talk to your doctor about your medical conditions before taking diuretics.
If you have lupus, diabetes, high cholesterol, or liver disease, you may not be a good candidate to take drugs in this class.
Side Effects – Diuretics
The common side effects of CKD diuretics can include:
- Diarrhea
- Tingling
- Headaches
- Blurred vision
- Constipation
- Loss of appetite
The severe side effects of the drugs include:
- High blood sugar
- Kidney and pancreas problems
- Hearing loss
- Muscle spasms
- Lightheadedness
- Easy bruising and bleeding
Drug Interactions – Diuretics
Diuretics can interact with many drugs, including but not limited to:
- Antibiotics
- Other diuretics
- Aspirin
- Phenytoin
- Blood pressure medications
Hormone Injections
To combat anemia in CKD patients, doctors may prescribe a hormone injection called erythropoietin (Eprex, Bimolin, Espogen, Ceriton, Hemax, and others).
This drug helps the body create more red blood cells. Sometimes, doctors will also prescribe an iron supplement to defeat anemia.
Warnings and Contraindications – Hormone Injections
Doctors do not prescribe this medication for patients who suffer from seizures. Cancer patients who receive hormone or radiation therapy should also avoid erythropoietin.
The drug is slow-acting. It cannot counter severe anemia or act as an emergency solution.
Side Effects – Hormone Injections
The common side effects of these injections are:
- Chest pain
- Rash
- Breathlessness
- Swelling of the tongue, lips, and throat
The drug can also cause headaches, flu-like symptoms, and bone pain, and it increases the risk of blood clots.
Drug Interactions – Hormone Injections
Erythropoietin can interact with several drugs, among them other hormone-based products.
The injections can interact with cyclosporine, methyltesosterone, and dichlorphenamide, among others.
Phosphate Binders
Healthy kidneys eliminate phosphates from the body. Diseased kidneys cannot function optimally, leading to high levels of phosphates in the blood. Doctors may prescribe phosphate binders to patients whose phosphate levels are abnormally high.
- Calcium acetate (Phoslo, Phoslyra, Calphron, Eliphos, and others)
- Calcium carbonate (Calci-chew, Os-Cal 500, and others)
Warnings and Contraindications — Phosphate Binders
You should not take phosphate binders like calcium acetate if your blood calcium levels are already high or you take digoxin.
Side Effects — Phosphate Binders
The common side effects of these drugs include:
- Diarrhea
- High calcium levels
- Nausea and vomiting
Some severe side effects are:
- Bone pain
- Constipation
- Exhaustion
- Increased thirst
- Muscle weakness
Drug Interactions — Phosphate Binders
Phosphate binders may interact with thyroid medications and some antibiotics, like tetracycline.
Steroids
Glomerulonephritis is the inflammation of the filters in the kidneys. This inflammation may be the result of an overactive immune system and can cause CKD.
To suppress the immune system and alleviate inflammation, doctors may resort to steroids. The steroid of choice for CKD is prednisolone. Doctors may also use low doses of an immunosuppressant called cyclophosphamide.
Warnings and Contraindications — Steroids
Doctors may not prescribe steroids like prednisolone for patients with high blood pressure, liver disease, thyroid problems, and osteoporosis. You should not take prednisolone if you have a fungal infection anywhere in your body.
Side Effects — Steroids
Prednisolone can cause a wide range of severe and common side effects, like:
- Seizures
- Tarry stools
- Bloody cough
- Shortness of breath
- Rapid weight gain
- Fluid retention
- Dizziness
- Headaches
- Constipation
- Unusually intense thirst
Drug Interactions — Steroids
Hundreds of drugs can interact with prednisolone. Of these, 66 are severe interactions and 440 are moderate. The drugs that can interact with prednisolone include antibiotics and other steroids.
Find the Best Prices for Chronic Kidney Disease Medications with BidRx

Chronic kidney disease medications are often at the cutting edge of medical technology. Consequently, they are pricey. Let BidRx find the pharmacies that can give you the lowest price for CKD medications.
How It Works
Sign up to BidRx and create a bid for your prescription. Pharmacies compete to fill your prescription for the lowest price. You simply compare prices and make your choice.
BidRx connects you with pharmacies across the country. You can buy your medications online or pick them up at your local drug store, depending on the offer you choose.
Find your CKD medicines on our medication page and place your bid today.