Highlights
- Simvastatin has been available in its generic form in the U.S. since 2006.
- Simvastatin helps with cholesterol management, preventing heart attacks and strokes.
- Simvastatin also has several off-label uses.
- This medication is safe for most people, but certain groups of people should not take simvastatin.
- As with all drugs, there are side effects and potential drug interactions that users should be aware of.
Simvastatin belongs to a class of medications known as statins. Statins work by inhibiting the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase. They lower LDL (bad) cholesterol levels in the blood and increase good (HDL) cholesterol levels. Simvastatin also lowers blood triglyceride levels.
Statins reduce the risk of life-threatening diseases like heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular problems.
What Is Simvastatin and What Is It Used For?
Akira Endo, a Japanese biochemist, discovered the precursor to simvastatin, mevastatin, in the 1970s. Mevastatin was an unstable compound that was difficult to produce.
The pharmaceutical giant Merck perfected mevastatin and named their more stable version simvastatin, sold under the brand name Zocor. The FDA approved Zocor for the U.S. market on December 31, 1991.
During the early 1990s, simvastatin was still undergoing clinical trials. As the patent holder, Merck had exclusive rights to market its product. That patent expired in 2006, allowing other pharma companies to produce generic versions of the drug. The resulting competition slashed prices, making simvastatin more affordable and readily available.
Simvastatin has helped millions of people worldwide avoid life-threatening heart attacks, strokes, and other severe cardiovascular events.
Simvastatin’s Off-label Uses
In addition to its cholesterol-controlling effects, simvastatin has shown anti-inflammatory and immune-modulating effects that have prompted researchers to look into it for other uses. It should be noted, though, that these effects are not well understood; more research is needed to determine the full extent of simvastatin’s immune-modulating effects.
Research is currently ongoing on the use of simvastatin for the following conditions:
- PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome) in women. Simvastatin helps PCOS sufferers avoid diabetes and improve their cholesterol levels.
- Multiple sclerosis (MS). As an anti-inflammatory agent, simvastatin can help fight this autoimmune disease of the central nervous system.
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In addition to its anti-inflammatory effects, simvastatin may also dampen the response of the immune system, helping doctors control autoimmune diseases.
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Simvastatin can help the liver get rid of accumulated fat while soothing inflammation.
How Does Simvastatin Work?

When you ingest simvastatin, the drug reaches your liver through your digestive system. There, it goes through an extensive transformation, metabolizing into simvastatin acid, its active form.
Simvastatin acid inhibits an enzyme called 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme. This enzyme determines to a significant degree how much cholesterol the liver produces.
With cholesterol production reduced, LDL receptors on liver cells become “hungry.” They gobble up more LDL cholesterol, reducing its levels in the blood.
In addition to removing more LDL cholesterol from the blood, simvastatin also increases HDL (good) cholesterol levels. High HDL cholesterol levels have protective effects on the cardiovascular system.
The anti-inflammatory effects of the drug help reduce inflammation in the blood vessels, further contributing to simvastatin’s cardiovascular protective effects.
Once the body uses up the drug, it eliminates the waste through feces and bile.
What Formulas Are Available for Simvastatin?
Simvastatin is mostly available in oral tablet form, in several dose strengths. At BidRx, the medication is available in 5 milligram, 10 milligram, 20 milligram, 40 milligram, and 80 milligram tablet forms, and as a 20 milligram per 5 milliliter oral liquid.
In addition to the oral tablets, simvastatin is available in several dose strengths as an oral disintegrating tablet (ODT) for patients who can’t swallow tablets.
For an even stronger cholesterol-lowering punch, some drug makers have combined simvastatin with ezetimibe, a different type of cholesterol-lowering medication, in a single tablet (brand name Vytorin). These combination tablets and ODTs are convenient for patients who require multiple medications to manage their cholesterol levels.
Simvastatin Dosage and Administration
The maximum adult dose for simvastatin is 40 milligrams per day, taken orally with water. In some cases, a doctor may prescribe a dose of 80 milligrams; however, the FDA has issued a warning about the increased risk of muscle injury with the 80 milligram dose.
The initial dose is typically 10 to 20 milligrams daily. Doctors can increase the initial dose depending on how patients respond to treatment. High-risk patients may receive 40 milligrams from the start.
If the treatment fails to achieve adequate LDL-cholesterol reduction with a 40 milligram dose, doctors may consider changing medications or adding an additional cholesterol-lowering agent.
Once an optimal dose is established, doctors may cut the initial daily dose to a 5 to 10 milligram maintenance dose.
Patients with the genetic disorder homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia may be started on a 40 milligram dose. For patients who have been using the drug for more than a year without significant side effects, doctors may increase the daily dose to 80 milligrams.
For pediatric homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia patients, the daily dose of simvastatin is generally 10 milligrams. The maintenance dose is typically 10 to 40 milligrams, and the maximum daily dose for children is 40 milligrams.
Simvastatin Dose Reduction
Doctors will adjust simvastatin dosage for a variety of reasons. Typically, they only do so in intervals of four weeks or more.
For patients with severe kidney problems, doctors may reduce the dose to 5 milligrams. Mild kidney problems don’t usually require a dose reduction.
Those with liver problems or significant intake of alcohol should not take simvastatin at all.
Some drug interactions may require doctors to lower patients’ daily dose of simvastatin by 50%.
In general, patients who take verapamil or diltiazem should not take more than 10 milligrams of simvastatin per day.
Patients taking amiodarone, ranolazine, or amlodipine may require a daily dose limit of 20 milligrams.
Talk to your doctor about all medications you take, including vitamins and dietary supplements. This information can be vital for establishing the right simvastatin dosage for you. Some medications rule out simvastatin as an option, requiring an alternative statin. (See Drug Interactions below.)
How Should I Take Simvastatin?
It is your doctor’s job to make it clear to you how you should take this drug. Follow the prescription closely, and don’t ever take more or less than your doctor prescribed. Taking less can reduce its cholesterol-lowering effects. Taking more can result in overdosing.
Take Zocor with meals unless your doctor advises otherwise. If you take one dose per day, take it before bedtime with a modest meal. If you take two doses per day, take them both with meals.
Your Zocor dosage may need to be changed periodically. To determine your optimal dose, your doctor may require frequent blood tests. Always follow your doctor’s instructions about how much Zocor to take and how to take it.
Don’t stop taking Zocor even if you feel well; you may need to take it for the rest of your life. However, your doctor may tell you to stop taking simvastatin before undergoing surgery or for other reasons.
What Are the Potential Side Effects of Simvastatin?
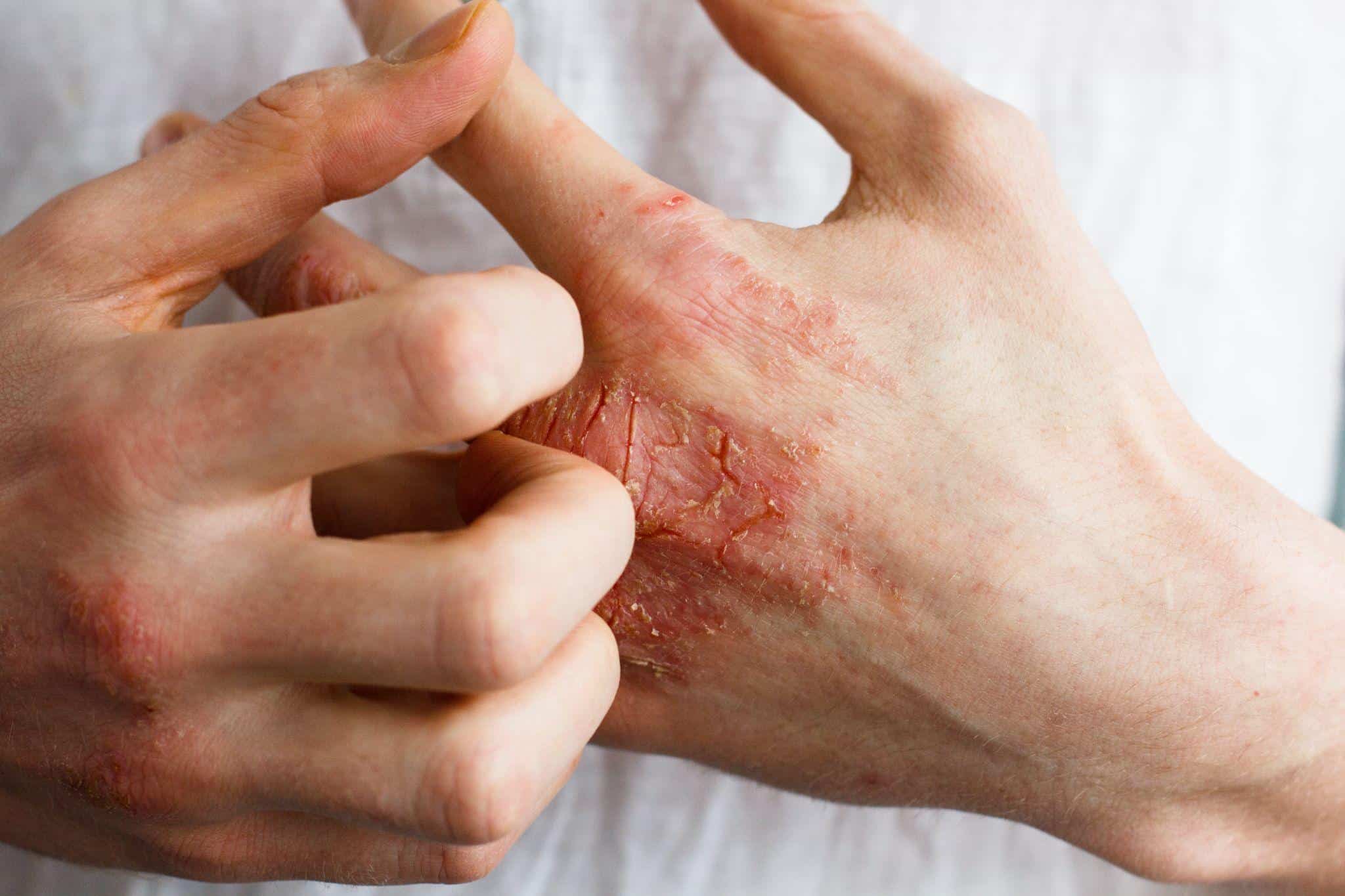
Like statins in general, simvastatin can trigger a wide range of severe and less-severe side effects. Some of its most common side effects are eczema and increased creatine phosphokinase (CPK) levels in the blood.
Severe side effects of the drug can include:
- Irregular heartbeats
- Fast heartbeats
- Fainting
- Feeling dizzy
Less-frequent severe side effects include:
- Chills
- Blurry vision
- Coughing
- Pain in the bladder
- Dark urine
- Headache
- Fever
- Flushing
- Inexplicably increased hunger or thirst
- Muscle spasms
- Swelling in the joints
- Vomiting
- Difficult breathing
- Fruity-smelling breath
- Sweating
- Pain in the lower back or sides
Other severe side effects, the frequency of which we don’t know, may be:
- Indigestion and bloating
- Diarrhea
- Light clay-colored stools
- Hive-like swelling
- Jaundice
- Upper-abdominal pain
- Ulcers
- Constipation
- Tightness in the chest
If you experience any of these side effects, contact your doctor and seek specialist help immediately. In extremely rare cases, simvastatin may lead to kidney failure.
The following less-severe side effects of simvastatin may not require medical attention. Listen to what your body tells you if you have these side effects. If they worry you or grow bothersome, contact your doctor.
- Acid reflux
- Bloating
- Digestive problems
- Skin rash
- Dizziness
- Pain in the eyes or cheekbones
- Feeling full without a reason
- Burning sensations in the chest or stomach
Other, less-frequent and less-severe side effects can include:
- Loss of sex drive
- Erectile dysfunction
- Hair loss
- Forgetfulness
- Depression
Side effect lists are never complete. If you have any new or unusual symptoms after beginning simvastatin, talk to your doctor.
What Should I Avoid When Taking Simvastatin?
Individuals taking simvastatin should avoid:
- Alcohol. Like alcohol, simvastatin taxes the liver, so drinking increases your risk of liver damage.
- Foods high in fat and cholesterol. The drug lowers your cholesterol levels to help you avoid cardiovascular problems. It is also part of a wider approach to lowering cholesterol.
- Grapefruit juice and products that contain grapefruit. Grapefruit can interfere with simvastatin and cause unexpected side effects.
What Should I Do If I Miss a Dose of Simvastatin?
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember it. If it’s almost time for your next dose, skip the missed one. Don’t try to make up for it by doubling a dose.
What Should I Do If I Overdose on Simvastatin?
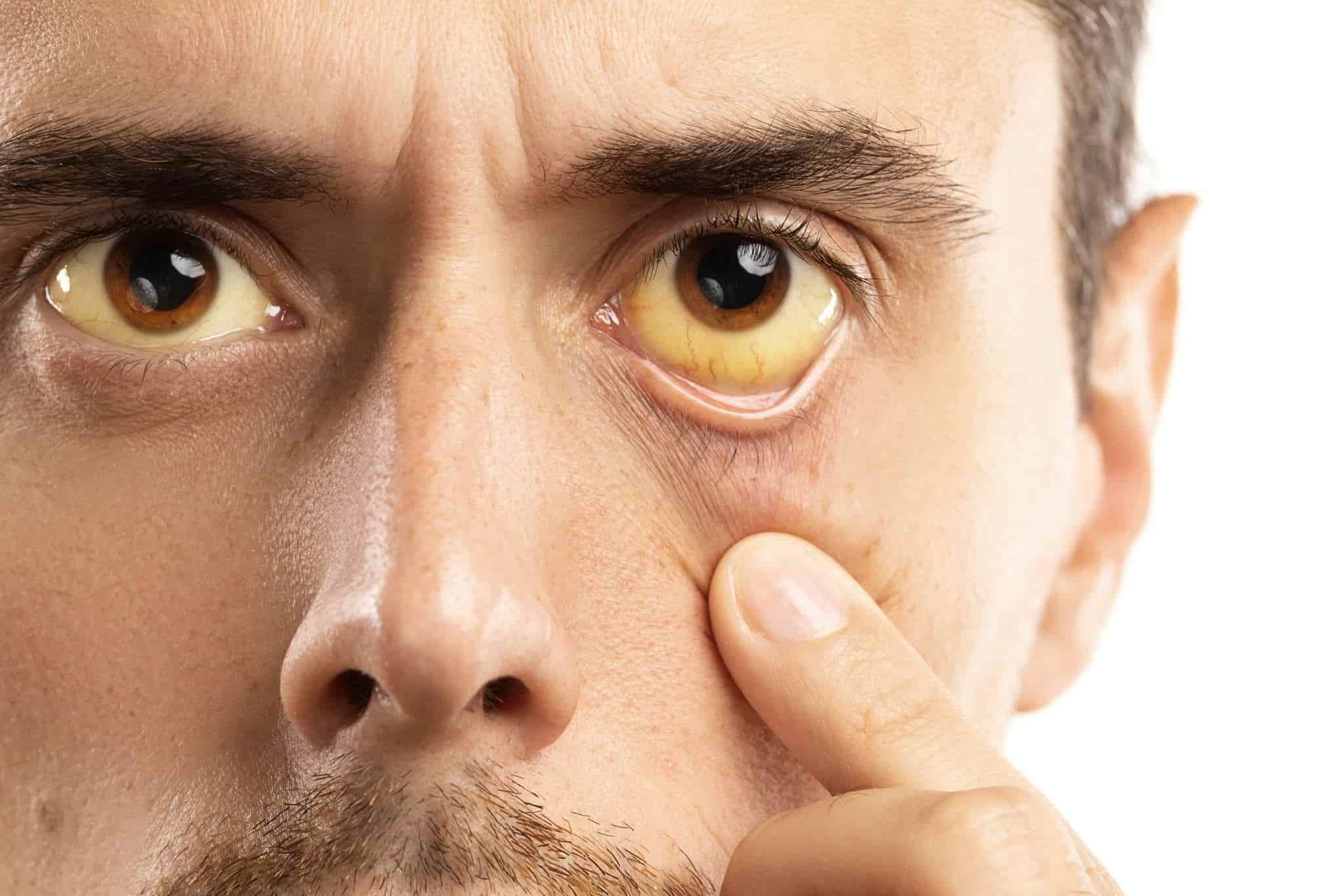
If you overdose on simvastatin, you may notice some of these severe side effects:
- Jaundice
- Pain in the upper right area of your stomach
- Headache
- Vomiting
- Clay-colored stools
Overdosing on this drug will likely damage your liver. If you suspect you have overdosed, seek immediate medical attention. If you can’t get to medical help, call the Poison Control Center at 1-800-222-1222.
Who Should Not Take Simvastatin?
If you are allergic to the drug, have active liver disease, or are pregnant, simvastatin is not for you. Pregnant women should avoid this medication, as it can harm unborn babies.
Also, tell your doctor if you ever had any of the following conditions:
- Liver disease
- Diabetes
- Kidney disease
- Alcoholism
- Thyroid problems
Tell your doctor if you drink alcohol daily. Also mention all medications, vitamins, and supplements you take.
Simvastatin can interact with other drugs and cause potentially dangerous side effects.
Are There any Potential Drug Interactions With Simvastatin?
We know about 299 drugs that can interact with simvastatin, including 57 that are considered major. Of these, amlodipine (Norvasc) may be the most dangerous, as its interaction with simvastatin can cause a significant increase of simvastatin levels in the blood. Elevated simvastatin levels can cause severe liver damage and may even trigger the breakdown of musculoskeletal tissue. This condition can cause kidney failure and even death.
Some of the symptoms of amlodipine and simvastatin interactions are:
- Pain and swelling in the joints
- Fever and chills
- Jaundice
- Dark urine
- Rashes and itching
- Vomiting
- Nausea
Other drug classes that are known to have potentially major interactions with simvastatin are:
- Calcium channel blockers. These drugs are used to treat high blood pressure and heart disease. They can increase the levels of simvastatin in the blood, which can increase the risk of side effects.
- Macrolide antibiotics. These drugs are used to treat infections. They can increase the levels of simvastatin in the blood, which can increase the risk of side effects.
- HIV protease inhibitors. These drugs are used to treat HIV. They can increase the levels of simvastatin in the blood, which can increase the risk of side effects.
- Azole antifungal agents. These drugs are used to treat fungal infections. They can increase the levels of simvastatin in the blood, which can increase the risk of side effects.
- Cyclosporine and cyclosporine-like agents. These drugs are used to prevent organ rejection after transplantation. They can increase the levels of simvastatin in the blood, which can increase the risk of side effects.
- Niacin (nicotinic acid) in high doses. This is a form of vitamin B3 that is used to lower cholesterol. It can increase the levels of simvastatin in the blood, which can increase the risk of side effects.
- Gemfibrozil and fenofibrate combination. These drugs are used to lower cholesterol. They can increase the levels of simvastatin in the blood, which can increase the risk of side effects.
While not a drug, grapefruit juice and products containing grapefruit can increase the levels of simvastatin in the blood, which can increase the risk of side effects.
Drug interaction lists are never complete. Be sure all your providers know all the medications and supplements you take, and keep them updated.
Get the Lowest Price for Simvastatin With BidRx

BidRx allows you to create a bid for the medications you need and lets pharmacies make their best offers. You get to choose the best deal for you and pick up your medications locally or have them delivered.
Here’s how to create a bid for simvastatin (Zocor): Create a BidRx account, log in, and select the medication you need from our medications page. Sign up to create your bid today.