Highlights
- Heart failure is the inability of the heart to supply other organs with enough blood.
- Heart failure medications relieve the heart of pressure, allowing it to pump adequate amounts of blood.
- Doctors prescribe heart failure medications to improve the quality of life of heart failure patients.
- Find the lowest prices for heart failure medications with BidRx.
Heart failure affects approximately 6.2 million people in the U.S. In 2018, close to 380,000 people died of heart failure. Medication is a first-line treatment for people with heart failure, and finding the right heart disease medications at a good price can be a lifesaver.
About Heart Failure Medications
Heart failure, commonly called congestive heart failure, happens when the heart loses the ability to pump enough blood to sustain the optimal functioning of the other organs. Heart failure doesn’t mean that the heart stops.
Those who experience congestive heart failure may complain of the following symptoms:
- Shortness of breath during strenuous activities
- Swelling of the feet, stomach, ankles, or legs due to water retention
- Fatigue
- Difficulty breathing when lying down
Chronic conditions like diabetes, alcoholism, coronary artery disease, and high blood pressure can cause heart failure, as can a myocardial infarction, commonly known as a heart attack.
Doctors can prolong the lives of heart failure patients and improve their quality of life through medication. The types of drugs doctors prescribe to treat heart failure range from ACE inhibitors to antiarrhythmics, vasodilators, and glucocorticoids.
ACE Inhibitors
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors improve the blood flow through the veins by dilating the blood vessels. By improving blood flow, they make it easier for the heart to pump blood to the other organs. ACE inhibitors counteract angiotensin, a substance that results from heart failure and narrows the blood vessels.
ACE inhibitors are powerful medications with potentially severe side effects. They are among the most essential and critical medications for the treatment of heart failure. They are all prescription-based.
- Lisinopril (Qbrelis, Zestril, and others)
- Enalapril (Epaned, Vasotec)
- Ramipril (Altace)
- Benazepril (Lotensin)
- Quinapril (Accupril)
- Captopril
- Perindopril
- Fosinopril
- Moexipril
- Trandolapril
Warnings and Contraindications – ACE Inhibitors
ACE inhibitors are potent medications that can harm unborn babies, so pregnant women should not take these drugs. Avoid ACE inhibitors if you have ever had angioedema. If you have kidney disease or diabetes, talk to your doctor about the medications you take for these conditions. Some diabetes and kidney disease drugs are not compatible with ACE inhibitors.
Many drugs can interact with ACE inhibitors and cause severe side effects. Always tell your doctors about all medications and supplements you take. Do not drink alcohol when taking ACE inhibitors.
Should you experience any unpleasant side effects, seek medical attention immediately.
Side Effects – ACE Inhibitors
The common side effects of ACE inhibitors include but are not limited to:
- Headaches
- Chest pain
- Coughing
- Dizziness
- Weakness
- Nervousness
- Heaviness in the legs
- Shortness of breath
- Reduced sense of taste during the early stages of the regimen
The list of severe, less-common side effects includes:
- Sore throat
- Fever
- Light-headedness and the sensation of passing out
- Liver problems, including jaundice
- Kidney problems
- High potassium levels that cause weakness and nausea
Ensure that your doctor monitors your blood pressure while you’re undergoing treatment with ACE inhibitors.
Drug Interactions – ACE Inhibitors
ACE inhibitors can interact with many drugs. Always disclose every drug and supplement you take to your doctor.
NSAIDs like ibuprofen, naproxen, and aspirin can limit the effects of ACE inhibitors. Other medications that may interfere with ACE inhibitors are:
- Gold injections for arthritis
- Insulin
- Diuretics
- Potassium supplements
- Drugs that prevent the body from rejecting transplanted organs
Calcium Channel Blocking Agents
Calcium channel blockers are drugs that reduce the workload of the heart by relaxing blood vessels. They also increase the supply of blood and oxygen to the heart.

Doctors may use calcium channel blockers to treat high blood pressure when other medications fail. Calcium channel blockers are not appropriate for patients whose heart failure occurs in the left ventricle.
There are many calcium channel blockers, all available only by prescription. The most common include:
- Amlodipine (Norvasc)
- Diltiazem (Cardizem, Cardizem CD, Dilacor XR, and others)
- Nifedipine
- Nicardipine (Cardene IV)
Warnings and Contraindications – Calcium Channel Blocking Agents
Doctors won’t prescribe calcium channel blockers to patients with systolic (left ventricle) dysfunction.
Calcium channel blockers do not go well with alcohol. Alcohol increases their side effects and lowers blood pressure further.
If you use calcium channel blockers for high blood pressure, do not stop using them once you feel better.
Some patients complain of worsening chest pain when beginning treatment with calcium channel blockers or when doctors increase the dose. If your chest pain gets worse, contact your doctor.
Side Effects – Calcium Channel Blocking Agents
Calcium channel blockers can cause severe drowsiness in some patients. Do not operate machinery if you take these drugs. Other common side effects of this class of drugs include:
- Chest pain
- Increased appetite
- Swelling of the feet and ankles
- Pounding heartbeats
- Lightheadedness
- Stomach pain
- Nausea
- Dizziness
The severe but less-common side effects can include:
- Slow heartbeats
- Breathing difficulties
- Coughing or wheezing
- Rashes
- Weight gain
If you experience severe side effects, seek medical attention immediately.
Drug Interactions – Calcium Channel Blocking Agents
Calcium channel blockers are potent medications that can have severe interactions with other drugs. Talk to your doctor about all medications and supplements you take before starting treatment with calcium channel blockers.
Calcium channel blockers can interact with:
- Other heart and blood pressure medications
- Nitroglycerin
- Simvastatin
Antianginal Agents
Angina is the narrowing of the coronary arteries. It places pressure on the heart, making it less capable of pumping blood. Patients with this condition will frequently complain of chest pain.
Antianginal agents like nitroglycerin relax and dilate the arteries, relieving the heart of the additional pressure.
All antianginal agents are prescription-only medications.
- Isosorbide mononitrate
- Nitroglycerin (Nitrostat, Minitran, Nitro-Bid, Nitro-Dur, and others)
- Isosorbide dinitrate (Isochron, Isoditrate, Dilatrate-SR, and others)
- Ranolazine (Ranexa, Aspruzyo Sprinkle)
Warnings and Contraindications – Antianginal Agents
Antianginal agents prevent and treat chest pain. If you find they don’t work after several doses, or your chest pain grows stronger, seek medical help immediately.
Patients suffering from the following conditions should not take antianginal agents:
- Anemia
- Increased pressure in the skull
- Circulation problems
- Low blood pressure
Some people may be allergic to these medications. Seek medical attention immediately if you notice allergic symptoms like difficulty breathing, wheezing, swelling of the tongue or throat, etc. People who take drugs for erectile dysfunction should also avoid antianginal agents.
Side Effects– Antianginal Agents
Some of the common side effects of antianginal agents are:
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Tingling
- Lightheadedness
- Flushing
- Fainting
The severe side effects of these drugs are:
- Blurred vision
- Heart attack symptoms like nausea, sweating, chest pain spreading to the jaw, etc.
- Slow heartbeats
- Pounding heartbeats
- Throbbing headaches that do not respond to treatment
Drug Interactions – Antianginal Agents
Antianginal agents like nitroglycerin can interact with many other medications. Always let your doctor know about all medications and supplements you take before taking antianginal agents. Some of the drugs that can interact with these medications include:
- Diuretics
- Aspirin
- Heparin
- Erectile dysfunction medications
- Medications for the treatment of headaches
- Antidepressants
- Blood pressure medications
- Medications for the treatment of blood clots
This list is not complete. In addition to these drugs and medication classes, antianginal agents can also interact with seemingly innocuous vitamins and herbal supplements. Drug interactions can cause severe health problems, so don’t treat them lightly.
Vasodilators
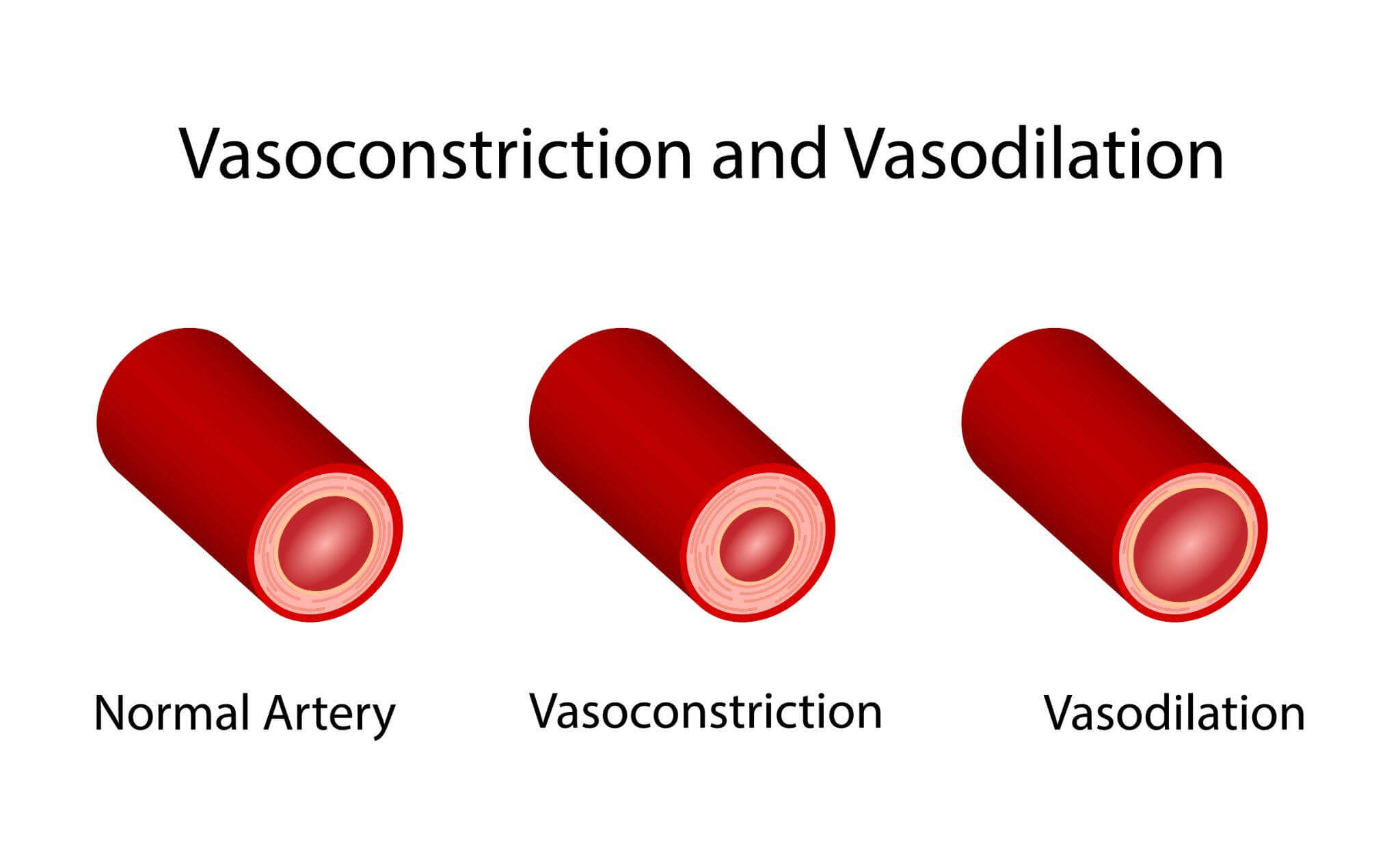 Vasodilators are medications that relax and dilate the blood vessels and arteries, allowing them to let more blood flow through. They make it easier for the heart to pump blood to the organs, alleviating pressure to treat congestive heart failure. Vasodilators can affect blood pressure, so it’s wise to keep tabs on it while taking them.
Vasodilators are medications that relax and dilate the blood vessels and arteries, allowing them to let more blood flow through. They make it easier for the heart to pump blood to the organs, alleviating pressure to treat congestive heart failure. Vasodilators can affect blood pressure, so it’s wise to keep tabs on it while taking them.
Tell your doctor about other medications you take. Some may interact with vasodilators and cause severe side effects, including death.
All vasodilators doctors use to treat heart failure are available only by prescription. There are many vasodilator medications, but they contain various formulations of just a few active drugs. They include:
- Hydralazine (Apresoline)
- Nitroglycerin (Nitro-Dur, Nitro-Time, Minitran, NitroMist, and others)
- Nitroprusside (Nitropress, Nipride RTU)
Warnings and Contraindications – Vasodilators
Doctors do not recommend vasodilators like hydralazine to patients with coronary artery disease. You should also avoid taking vasodilators if you suffer from rheumatic heart disease.
Let your doctor know if you suffer from any of these conditions:
- Kidney disease
- Lupus
- Chest pain
- Stroke
Pregnant and lactating women should avoid vasodilators because the drugs can pass into breast milk and affect the baby.
Side Effects – Vasodilators
Vasodilators can have a profound impact on the body. Their side effects can be similarly profound and disruptive.
Some of the severe side effects of these drugs include:
- Painful urination and reduced urine volume or no urination
- Fast heartbeats
- Lightheadedness
- Tingling and burning sensations in the extremities
- Joint pain or swelling
- The swelling of various glands
- Chest pain that spreads to the jaw and shoulder
If you experience any of these severe side effects, seek medical help immediately.
The more common side effects of vasodilators include but are not limited to:
- Headaches
- Poor appetite
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Chest pain
- Pounding heart
Drug Interactions – Vasodilators
Vasodilators don’t work well with other blood pressure medications. They can interact with diazoxide and various MAO inhibitors like linezolid, methylene blue injections, and phenelzine.
This list is far from complete. Vasodilators can interact with vitamins, herbal products, and dietary supplements. Tell your doctor about all the medications and supplements you take.
Group IV Antiarrhythmics
Group IV antiarrhythmics are calcium channel blockers. Doctors use these medications to treat an array of heart conditions, including irregular heartbeats, fast heartbeats, and high blood pressure.
By slowing the calcium channel current, group IV antiarrhythmics interfere with heartbeats, shortening some phases and prolonging other phases of the cardiac action. They also relax the muscles of the heart and the blood vessels.
Doctors only use one group IV antiarrhythmic to treat heart failure — diltiazem (Cardizem, Cardizem CD, Diltzac, Diltia XT, and others). Diltiazem is a prescription-only medication.
Warnings and Contraindications – Group IV Antiarrhythmics
Diltiazem can have serious effects on the body. It can interfere with thinking and reasoning. It can affect reactions and alertness, so do not drive a vehicle or operate machinery while taking this drug.
Keep using the medication even if you feel well. Don’t discontinue its use suddenly; it can lead to a sudden worsening of your condition.
Diltiazem is not a good option if you have low blood pressure or suffer from certain heart conditions. Tell your doctor if you suffer from any of the following:
- Liver disease
- Kidney disease
- Any condition you treat with digoxin or beta-blockers
If you’ve had a heart attack or have fluid in your lungs, your doctor will not prescribe diltiazem.
The drug can affect unborn babies, so it’s not an option for pregnant women.
Side Effects – Group IV Antiarrhythmics
Diltiazem’s severe side effects include:
- Light-headedness and the sensation of passing out
- Rapid weight gain
- Upper stomach pain
- Clay-colored stools and dark urine
- Jaundice
- Sore throat
- Fever
- Slow heartbeats or fluttering in your chest
- Shortness of breath
This list is not complete. Seek medical attention if you experience any of these side effects.
The more common and less-severe side effects of the drug include:
- Rash
- Nausea
- Weakness
- Dizziness
- Swelling
Drug Interactions – Group IV Antiarrhythmics
Some of the common medications that interact with group IV antiarrhythmics are:
- Beta-blockers
- Anti-anxiety medications
- Anesthesia medications
- Cholesterol medications called statins
Drugs like diltiazem can also interact with various vitamins, dietary supplements, and herbal products.
Group III Antiarrhythmics
Group III antiarrhythmics are potassium channel blockers. Like class IV antiarrhythmics, these drugs interfere with the heartbeat, correcting rhythm-related problems. Doctors use one of them, digoxin (Digitek, Lanoxin, Digox) to treat congestive heart failure.
Digoxin helps the heart produce stronger and more consistent beats. It is available only by prescription.
Warnings and Contraindications – Group III Antiarrhythmics
Although it is a medication that corrects heart arrhythmias, digoxin is not suitable for all arrhythmias. Your doctor will determine whether it’s the right choice for you.
Let your provider know if you’re suffering from any of these conditions:
- Thyroid problems
- Kidney disease
- Slow heartbeats and fainting
- Electrolyte imbalance
- Vomiting or diarrhea
- Fast heartbeats with a sudden onset
Side Effects – Group III Antiarrhythmics
Digoxin can cause a variety of side effects, some of which are severe. Severe side effects include:
- Tarry stools, indicating bleeding
- Stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
- Lightheadedness
- Arrhythmic heart rate
- Hallucinations and confusion
- Blurred vision and other vision-related problems
- Breast tenderness and swelling
Contact your doctor immediately if you notice any of these side effects. The less severe side effects of the drug include:
- Dizziness
- Weakness
- Depression
- Rashes
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
Drug Interactions – Group III Antiarrhythmics
Digoxin can interact with many drugs. Let your doctor know if you’re taking any other medications while undergoing treatment with digoxin. Be sure to mention any vitamins, herbal products, and dietary supplements you may take.
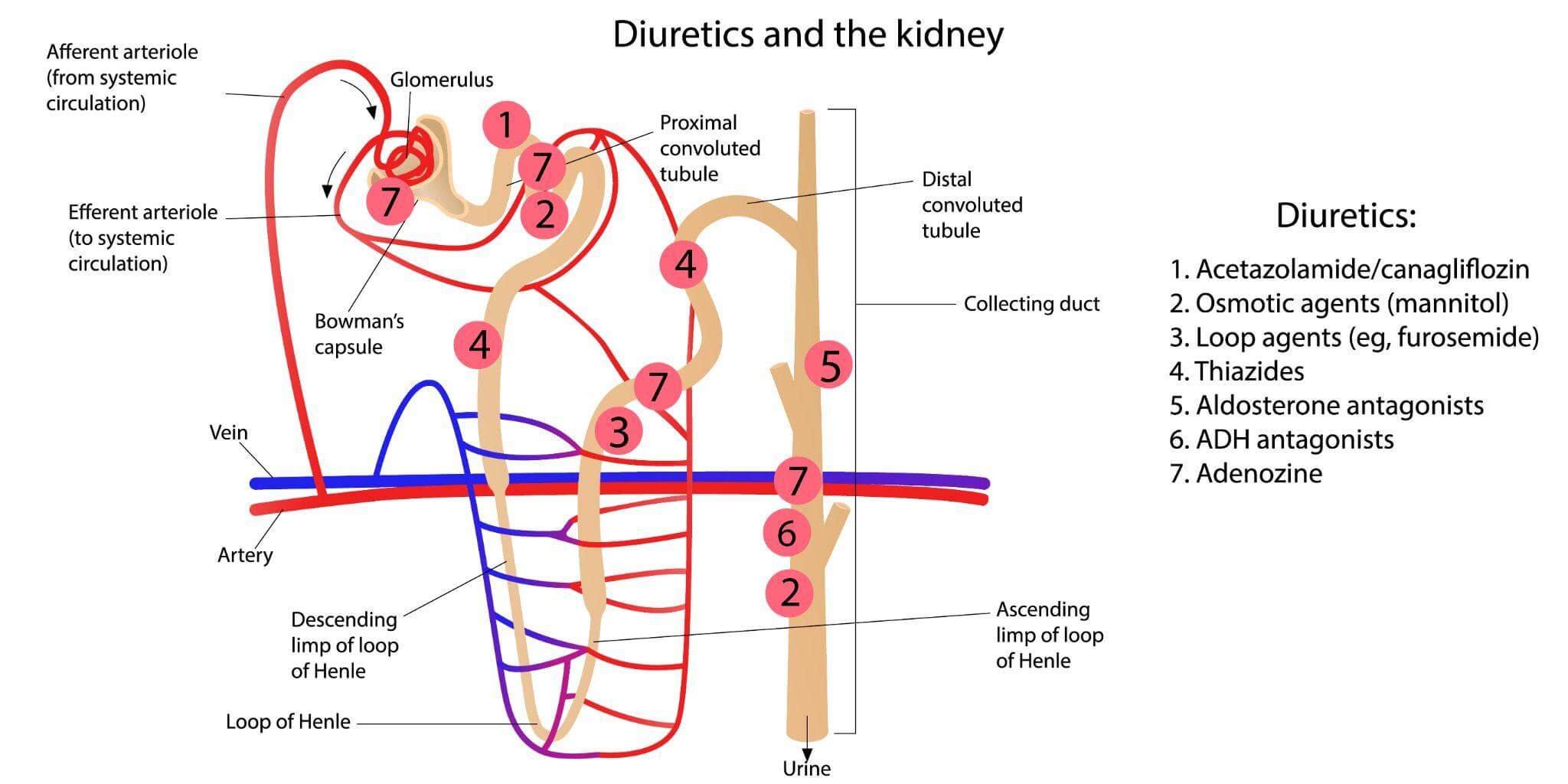
Potassium-sparing Diuretics
Diuretics are first-line treatment for mild hypertension and heart failure. Medications like potassium-sparing diuretics can prevent arrhythmias while maintaining the dry body weight of patients. These drugs can protect the cardiovascular system from the effects of aldosterone, and they can lower the risk of death from heart failure.
Potassium-sparing diuretics are prescription-only medications. They include:
- Spironolactone (Aldactone, CaroSpir)
- Eplerenone (Inspra)
- Amiloride (Midamor)
Warnings and Contraindications – Potassium-sparing Diuretics
Before taking potassium-sparing diuretics, talk to your doctor about your other health conditions. If you have diabetes, severe kidney disease, or high potassium levels, you cannot take these drugs.
If you have liver disease, high cholesterol, or take heart and blood pressure medications, you are also a poor candidate for treatment with potassium-sparing diuretics.
These medications can be dangerous for unborn babies and pregnant women. They may also interact with many other drugs, so it’s a good idea to talk to your doctor about the drugs you take before starting treatment.
If you show signs of an allergic reaction, seek medical help immediately.
Side Effects – Potassium-sparing Diuretics
The severe side effects of these drugs include allergic reactions like:
- Swelling of the tongue, mouth, throat, and face
- Trouble breathing
- Severe stomach pain
- Hives
Other severe side effects are:
- Nausea
- Irregular heartbeats
- Lightheadedness
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Swelling of the feet
- Inability to urinate
Contact a doctor as soon as possible if you experience these side effects.
The more common side effects of potassium-sparing diuretics include:
- Headache
- Dizziness
- High potassium levels
Drug Interactions – Potassium-sparing Diuretics
Potassium-sparing diuretics can interact with many drugs, dietary supplements, and vitamins. Some of these interactions can be severe.
Some of the drugs that interact with potassium-sparing diuretics are:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs)
- Blood pressure and heart disease medications
- Lithium
This list is not complete, so be sure your doctor is aware of all medications and supplements you take.
Inotropic Agents
 Doctors prescribe inotropic agents to patients who have recently had a heart attack or those suffering from congestive heart failure. Inotropic agents strengthen the contractions of the heart. They help the heart pump more blood to the organs to alleviate the effects of heart failure.
Doctors prescribe inotropic agents to patients who have recently had a heart attack or those suffering from congestive heart failure. Inotropic agents strengthen the contractions of the heart. They help the heart pump more blood to the organs to alleviate the effects of heart failure.
Inotropic agents can also help prepare advanced heart failure patients for therapies like heart transplants.
These drugs can have severe side effects and interactions. They are available only by prescription. Doctors may prescribe these medications after other heart failure medications have failed to work.
Inotropic agents include:
- Digoxin (Digitek, Lanoxin, Digox)
- Dobutamine (Dobutrex)
- Milrinone
Warnings and Contraindications – Inotropic Agents
Doctors should monitor your vital signs while you’re taking these drugs. You may develop an allergy to inotropic agents. If you do, stop taking the drugs and seek medical help.
Tell your doctor if you have any of these conditions:
- Heart valve disorders
- Asthma
- High blood pressure
Inotropic agents may not be safe for pregnant women.
Side Effects – Inotropic Agents
In addition to allergic reactions like hives, facial swelling, the swelling of the tongue and throat, and difficulty breathing, inotropic agents can cause many severe side effects:
- Tightness in the chest
- Lightheadedness
- Blurred vision
- Skyrocketing blood pressure
- Wheezing
- Swelling
- Rapid weight gain
- Seizures
Seek medical help if you experience any of these.
The common side effects include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Headaches
- Fever
- Tingling
Drug Interactions – Inotropic Agents
Always talk to your doctor about the treatments you follow and drugs you take before you begin treatment with inotropic agents. These drugs can interact with many other drugs, including vitamins, herbal supplements, and over-the-counter products. Some of the interactions can be severe.
Loop Diuretics
Loop diuretics help remove fluids from the body. They also eliminate salt from the body, making it easier for the heart to pump blood. In addition to treating water retention and swelling, these medications also treat high blood pressure.
Loop diuretics are prescription-only medications.
- Furosemide (Furoscix, Lasix, Lo-Aqua, and others)
- Torsemide (Soaanz, Demadex)
Warnings and Contraindications – Loop Diuretics
If you have difficulties urinating, you should avoid loop diuretics. Talk to your doctor if you suffer from any of the following:
- High cholesterol
- Liver disease
- Urination problems
- Enlarged prostate
- Diabetes
- Kidney disease
- An allergy to sulfa drugs
Your doctor will also want to know whether you recently had a radioactive dye injected into your veins for imaging purposes.
Pregnant and lactating women should avoid these medications.
Side Effects – Loop Diuretics
If you notice allergic symptoms like the swelling of your face, throat, tongue, or lips, seek medical attention immediately.
Loop diuretics may cause other severe side effects, including:
- Kidney problems
- Liver or pancreas problems, with symptoms like jaundice, upper stomach pain, dark urine, nausea, vomiting
- Muscle spasms
- Hearing loss
- High blood sugar, with symptoms like thirst, dry mouth, fruity breath
- Unusual bleeding
- Lightheadedness
The common side effects of these medications include:
- Blurred vision
- Diarrhea
- Dizziness
- Constipation
- Loss of appetite
Drug Interactions – Loop Diuretics
Loop diuretics don’t go well with:
- Other diuretics
- Some cancer medications
- Injected antibiotics
- Blood pressure and heart medications
- Aspirin
The list is not complete. Loop diuretics can interact with herbal products, dietary supplements, vitamins, and over-the-counter products.
SGL2 Inhibitors
Doctors use SGL2 inhibitors to increase cardiac blood flow. These medications act as mild diuretics, reducing the amount of sodium in the blood. SGL2 inhibitors can reduce the risk of major cardiac events in heart failure patients. Doctors use them as part of a foundational therapy for heart failure.
SGL2 inhibitors are available only by prescription.
- Dapagliflozin (Farxiga)
- Empagliflozin (Jardiance)
Warnings and Contraindications – SGL2 Inhibitors
SGL2 inhibitors can cause dehydration and other severe side effects. Do not take these drugs if you are in one of the following situations:
- You take blood pressure medications, including diuretics
- You have problems with your kidneys
- You are on a low-salt diet
- You are older than 65
Be aware that SGL2 inhibitors can cause vaginal and penile yeast infections.
Side Effects – SGL2 Inhibitors
SGL2 inhibitors can have severe side effects, including ketoacidosis, a condition that boosts the levels of ketones in the blood and urine. Ketoacidosis requires hospitalization and can lead to death.
Another potentially deadly side effect of SGL2 inhibitors is necrotizing fasciitis. If you notice tenderness, swelling, or redness in your perineum, the area between your anus and genitals, while taking an SGL2 inhibitor, seek medical attention immediately.
- Vomiting
- Nausea
- Abdominal pain
- Difficulties breathing
- Severe urinary tract infections requiring hospitalization
- Low blood sugar
- Fast heartbeats
- Confusion
- Sweating
- Shakiness
- Irritability and hunger
Some more common side effects of SGL2 inhibitors are:
- Sore throat
- Nasal congestion
- Yeast infections of the genitals (male and female)
- Changes in urination habits
Drug Interactions – SGL2 Inhibitors
Hundreds of drugs, vitamins, supplements, and herbal products can interact with SGL2 inhibitors. Inform your doctor of all the medications and over-the-counter products you take before beginning treatment with an SGL2 inhibitor.
Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs)

ARBs work to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, and kidney disease by reducing the action of the hormone angiotensin II. Angiotensin II constricts the blood vessels, allowing less blood through. ACE inhibitors also suppress the action of this hormone, but ARBs achieve the same effect through a different path.
ARBs block the receptors that allow angiotensin II to exert its effects. These receptors are in the blood vessels, heart, and kidneys. With the receptors blocked, the hormone can’t constrict the blood vessels. The relaxed blood vessels allow more blood through, making it easier for the heart to pump blood to other organs in the body.
ARBs are prescription-only medications that include:
- Valsartan (Diovan)
- Candesartan (Atacand)
Warnings and Contraindications – Angiotensin Receptor Blockers
Pregnant women and diabetics should not use ARBs. You may not be a good candidate for treatment with ARBs if you:
- Are on a low-salt diet
- Have a kidney disease
- Have a heart disease other than the one ARBs aim to treat
Side Effects – Angiotensin Receptor Blockers
ARBs can cause some severe side effects like:
- High potassium
- Lack of urination
- Lightheadedness
Seek medical attention if you experience these side effects. The more common and less severe side effects of these drugs include:
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Tiredness
- Flu symptoms
- Abnormal kidney test results
- Coughing
Drug Interactions – Angiotensin Receptor Blockers
ARBs can interact with other medications that lower blood pressure. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like aspirin, diclofenac, and ibuprofen may also interact with ARBs.
Diuretics can also interfere with ARBs.
Coumarins and Indandiones
These drugs are anticoagulation agents that prevent thrombosis in heart failure patients. By eliminating the risk of blood clots, they help the heart pump more blood and work optimally.
Coumarins and indandiones are prescription-only medications. There is only one drug in this class doctors may prescribe for heart failure: warfarin (Jantoven, Coumadin).
Warnings and Contraindications – Coumarins and Indandiones
Patients prone to bleeding cannot use warfarin. The drug increases the risk of severe bleeding. In some cases, it can be fatal. Do not take drugs like warfarin if:
- You have high blood pressure
- You had recent surgery on your spine, eye, or brain
- You find it impossible to take the drug at the same time every day
- You have a low red blood cell count
- You have stomach ulcers or urinary tract problems
People older than 65 should avoid drugs like warfarin if possible.
Side Effects – Coumarins and Indandiones
Warfarin is a blood thinner and can increase the risk of bleeding. Bleeding can be fatal in some patients.
Other serious side effects of Coumarins and Indandiones are:
- Swelling and bruising
- Sudden headaches
- Bleeding from small wounds that won’t stop
- Blood in the stool or urine
- Bleeding nose
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding
Drug Interactions – Coumarins and Indandiones
Coumarins and indandiones can interact with many drugs like other blood thinners, antibiotics, vitamin K supplements, and various herbal products.
Cardioselective Beta Blockers
Cardioselective beta blockers inhibit the beta 1 receptors in the heart. By doing so, they treat arrhythmias, high blood pressure, heart failure, and heart attacks. Cardioselective beta blockers are all prescription-only heart failure medications.
Doctors may prescribe two cardioselective beta blockers for heart failure.
- Metoprolol (Kapspargo Sprinkle, Toprol-XL)
- Bisoprolol
Warnings and Contraindications – Cardioselective Beta Blockers
You should not use these drugs if you have:
- Heart failure requiring hospitalization
- Circulation problems
- Slow heartbeats that can cause fainting
- Other serious heart problems
Talk to your doctor about all other conditions you may have.
Side Effects – Cardioselective Beta Blockers
The severe side effects these drugs can cause include:
- Cold hands and feet
- Lightheadedness and fainting
- Slow heart rate
- Rapid weight gain
- Difficulty breathing
Some common side effects are:
- Nightmares
- Depression
- Confusion
- Diarrhea
- Sleep problems
Drug Interactions – Cardioselective Beta Blockers
Cardioselective beta-blockers can interact with many medications, like:
- Other blood pressure medications
- Antidepressants
- Epinephrine
- MAO inhibitors (MAOIs)
Miscellaneous Cardiovascular Agents
Ivabradine (Corlanor) is a cardiovascular agent that can slow heart rate without reducing blood pressure. It reduces hospitalizations in patients who suffer from chronic systolic heart failure.
Warnings and Contraindications – Miscellaneous Cardiovascular Agents
Patients with low heart rates should not use ivabradine because it can interfere with a healthy heart rate.
Other conditions that would disqualify you as an ivabradine candidate are:
- Very low blood pressure
- Having a pacemaker
- Liver disease
Side Effects – Miscellaneous Cardiovascular Agents
Ivabradine can cause serious side effects, including:
- Pounding heartbeats
- Slow heartbeats
- Tightness in the chest
- Blurred vision
- Dizziness
- Tiredness
Some common side effects are:
- Light sensitivity
- High blood pressure
- Irregular heartbeats
Drug Interactions – Miscellaneous Cardiovascular Agents
Ivabradine can interact with:
- Asthma medications
- Medications for high blood pressure
- Depression medications
- HIV drugs
- Malaria medication
Find the Lowest Prices for Heart Failure Medications

Heart failure drugs are prescription-only medications that can have profound effects on the body. Some represent the cutting edge of medical science, and they can be expensive. Shop around before you buy your heart failure medications and compare prices.
Let BidRx Help You Find the Lowest Heart Failure Medication Prices
Sign up for BidRx. Find your heart failure medicines on our medication page and create a bid for the medications you need.
BidRx allows you to compare the prices competing pharmacies offer and choose the one you prefer.
BidRx connects you with pharmacies across the country, allowing you to order your medications online, locally, through specialty service, or by mail order. Find the lowest prices for your heart failure medications by placing a BidRx bid today!